JOURNAL 1632
Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2020 Issue: 2 July-December
p.133 - 141
Viewed 3679 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
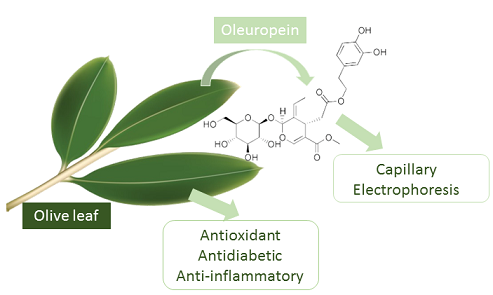
ABSTRACT
Oleuropein, the major active compound in olive leaf, has been of considerable interest for its many health benefits. This work aims the determination of oleuropein in olive leaves from Turkey by a rapid and simple capillary electrophoretic method, and then to correlate the oleuropein amounts and the bioactivities of olive leaf extracts. The optimal separation medium was composed of 30 mmol/L borate (pH: 9.6), 25 mmol/L2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (2-HP-β-CD), 10% (v/v) methanol. Moreover, olive leaf extracts were examined for antioxidant, antidiabetic, and anti-inflammatory activities. The antioxidant activities were determined by 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging activity. The antidiabetic activities were predicted using α-glucosidase inhibitory effects. For the anti-inflammatory activities of the extracts, their reduction power of pro-inflammatory tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha were measured. Oleuropein concentration ranged between 11.7-106 mg/g dry leaf. Strong correlations were detected between each biological activity and the oleuropein content of olive leaves
KEYWORDS
- Capillary electrophoresis
- Olive leaf
- Oleuropein
- Antioxidant activity
- Anti-inflammatory activity
- Antidiabetic activity