Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Reports
A scientific open access journal in the field of Bioorganic and Medicinal ChemistryLATEST ARTICLES
Proximate, phytochemical and sensory evaluations of African Black Pepper (Piper guineense), Guinea Pepper (Xylopia aethiopica) and Aidan Fruit (Tetrapleura tetraptera)spiced drinks

This study evaluated the proximate and phytochemical properties of African black pepper (Piper guineense), Guinea pepper (Xylopia aethiopica) and Aidan fruit (Tetrapleura tetraptera) spices and also assessed the level of acceptability of the drinks prepared using these spices. Pineapple, zobo and kunuzaki drinks enriched with African black pepper, guinea pepper and aidan fruitandginger/garlic (control) were produced. Proximate and phytochemical properties of the spices and sensory evaluations of the spiced drinks were determined. The results of the proximate compositions of the spices showed that aidan fruit recorded the highest values in moisture (11.33%), ash (8.53%) and protein (9.78%). African black pepper recorded highest values in fat (9.32%) and carbohydrate (58.95%) while Guinea pepper recorded highest values in fibre (19.60%). African black pepper recorded the lowest values in moisture (9.45%), ash (6.83%), Fibre (8.64%) and protein (6.82%). The phytochemical properties of the spices showed that African black pepper recorded the highest values in alkaloids (1.77%), tannins (1.85%), saponins (0.21%) and flavonoids (0.47%) while Guinea pepper recorded the highest values in cyanide (0.05%) and phenol (3.81%) and Aidan fruit recorded the lowest values for all the phytochemical determined. The sensory evaluation showed that sample B (stimulating pineapple drink enriched with uziza, uda and oshosho) was most preferred by the panelists. Findings from this study have clearly shown that these spices can be used in production of various drinks with comparable nutritional qualities and general acceptability to the already existing drinks.
DOI htpp://doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.35.2505.3539 Keywords African black pepper Guinea pepper Aidan fruit zobo kunuzaki DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Novel multi-axis therapeutic targeting approaches in Candida albicans: emerging dual-target strategies to overcome antifungal resistance
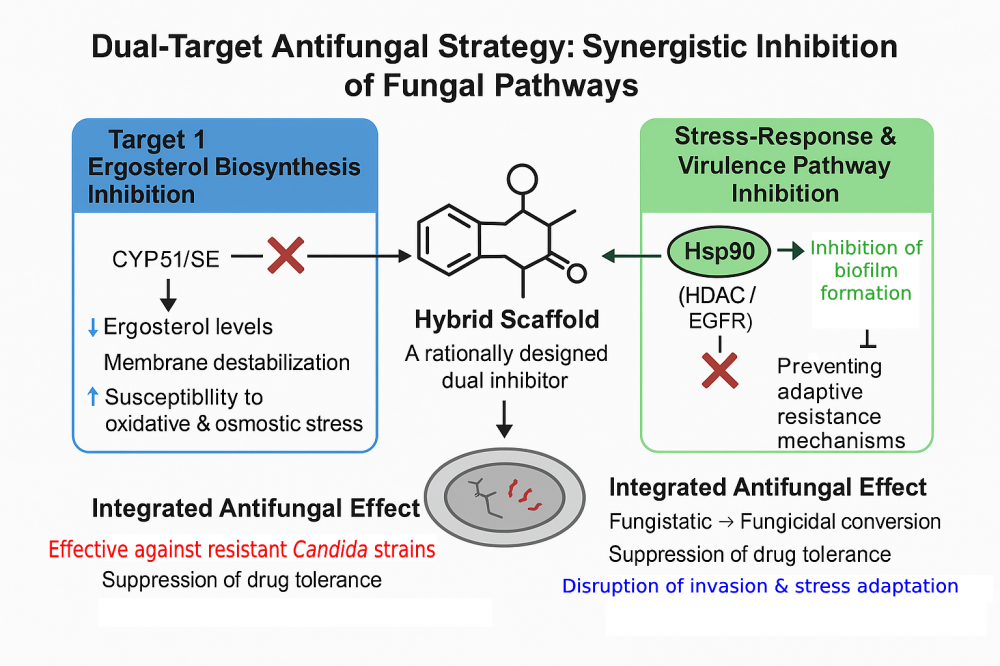
Global climate change, the increasing prevalence of immunosuppressed patient populations, and mounting environmental selection pressures have collectively enhanced the adaptive capacity of pathogenic fungi (most notably Candida albicans) transforming invasive fungal infections into a major global clinical threat. The limited chemical diversity and narrow target spectrum of current antifungal agents, particularly those acting through a unidirectional mechanism centered on CYP51 inhibition, facilitate the rapid emergence of drug resistance. C. albicans simultaneously activates a network of interconnected resistance mechanisms to survive antifungal exposure. CYP51 point mutations and gene amplification, overexpression of efflux pumps, HSP90–calcineurin–dependent stress adaptation, and epigenetic reprogramming mediated by HDAC/HAT imbalance constitute the core components of this defensive architecture. Moreover, the central regulatory role of the EGFR–MAPK axis in epithelial invasion underscores that C. albicans pathobiology extends far beyond metabolic pathways, relying instead on the coordination of a sophisticated signaling network. This multilayered defense system inherently restricts the efficacy of single-target antifungal agents. Consequently, combination therapies that simultaneously engage distinct biological pathways hold the potential to enhance antifungal efficacy through pharmacodynamic synergy. However, substantial variability in clinical responses, drug–drug interactions and limited translational evidence have hindered the routine implementation of combination regimens in clinical practice. These constraints have positioned dual-target antifungal design as a more rational and feasible alternative. Notably, clinical evidence supports multi-axis antifungal engagement, with late-stage pipelines advancing toward novel resistance-relevant targets such as the Phase 3 Gwt1 inhibitor fosmanogepix. Recent studies on dual active architecture, including CYP51 and HDAC, HSP90 and HDAC, CYP51 and SE, as well as CYP51 and HSP90, identify four core axes governing C. albicans fitness: ergosterol biosynthesis, epigenetic regulation, proteostatic stress response, and epithelial invasion. Coordinated modulation of these axes results in synergistic suppression of antifungal resistance and virulence. In this review, we provide an integrated evaluation of the molecular foundations of antifungal resistance in C. albicans, the pharmacodynamic advantages of combination therapies, and the therapeutic promise of dual-target design strategies. Collectively, the evidence supports multi-target antifungal strategies as a transformative paradigm capable of achieving durable, resistance-agnostic efficacy.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.36.2512.3745 Keywords Invasive fungal infection histone deacetylase ergosterol lanosterol 14α-demethylase dual inhibitors DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.In silico prediction of some peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) agonists targeted drugs as potential SARS-Cov-2 inhibitors
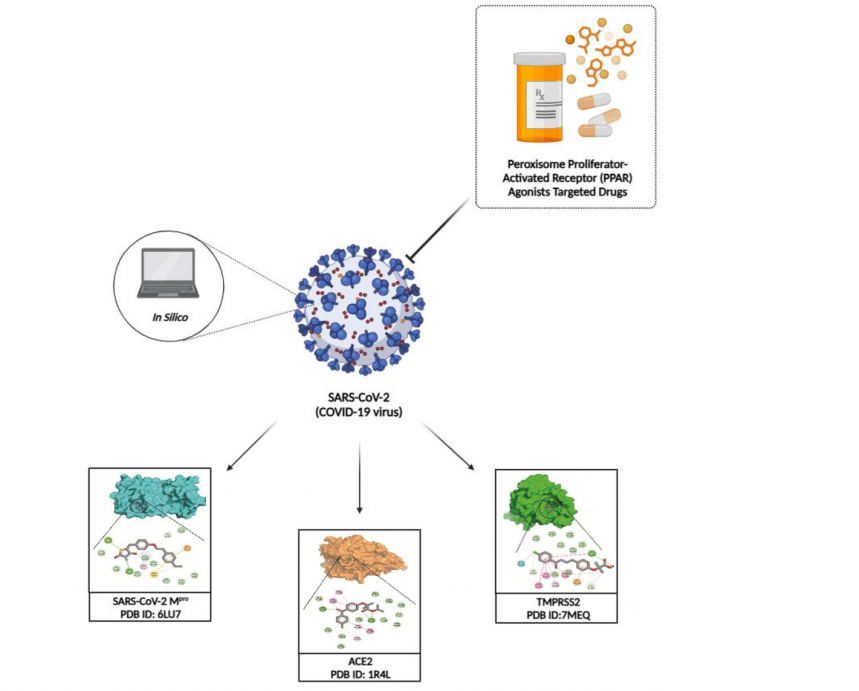
Since COVID-19 epidemic began, no effective medication have been found to treat this disease. In the current study, several peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) agonist drugs, including fenofibrate, binifibrate, bezafibrate, ciprofibrate, clofibrate, gemfibrozil, pioglitazone, and rosiglitazone were selected, and the molecular docking studies were applied by using main protease (Mpro), human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), and transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) targets. The chemical structures of selected drugs were retrieved from the PubChem database (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). AutoDock 4.2 molecular docking program was used to obtain best binding interactions of selected drugs. Visualization of the docking results was performed using BIOVIA Discovery Studio Visualizer and PyMol. As a result, rosiglitazone and binifibrate were found to be an effective drugs against SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) with binding energies of –6.8 and -6.7 kcal/mol, respectively. Bezafibrate and binifibrate were found to be an effective drugs against ACE2 with binding energies of -8.6 kcal/mol, respectively. On the other hand, fenofibrate, bezafibrate and rosiglitazone showed highest binding energies against TMPRSS2 protein as compared with reference drugs favipiravir, chloroquine, and hydroxychloroquine. Our in silico results suggest that PPAR agonist drugs warrant further investigation as potential lead molecules for discovering more potent compounds in anti-CoV drug development research.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.34.2502.3426 Keywords SARS-CoV-2 molecular docking ACE2 TMPRSS2 DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of synthetic 2-styrylchromones
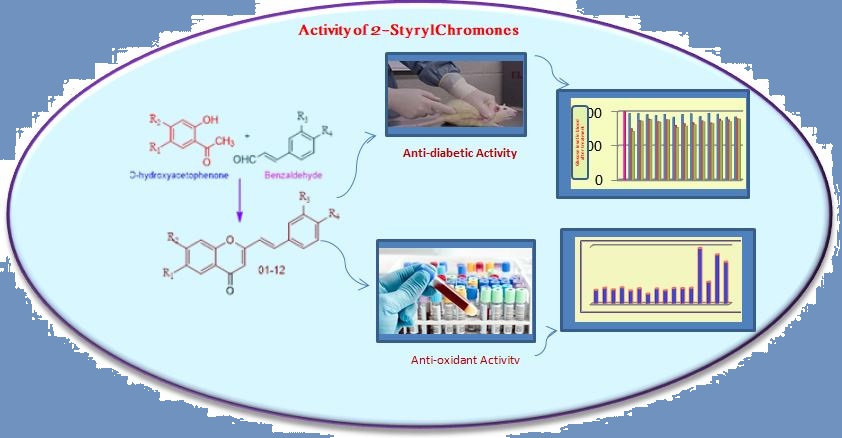
2-Styrylchromones are very potent bioactive substances showing innumerable activities like antioxidant, antidiabetic, antiviral, antiinflammatory, anticancer, anti-microbial etc. All these activities are due to their core structure (benz-γ-pyrone) containing styryl group at 2nd position. Substituents especially hydroxyl groups are responsible for anti-diabetic and antioxidant activities. 2-Styrylchromones with a greater number of –OH substituents showed high activity than the remaining compounds. Compounds 5, 6, 7 and 9 having significant activity where the nature and position of substituents play a vital role. The synthetic compound with –OH groups at 4', 6 and 7 positions competed with standard drugs in respective activities.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.36.25.05.3509 Keywords 2-styrylchromones antidiabetic Activity antioxidant Activity streptozotocin induced diabetic glibenclamide superoxide radical scavenging DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.