Records of Natural Products
A scientific open access journal in the field of natural products.LATEST ARTICLES
A new antifungal α-pyrone secondary metabolite isolated fromthe tobacco-derived fungus Aspergillus aculeatus Aa-1
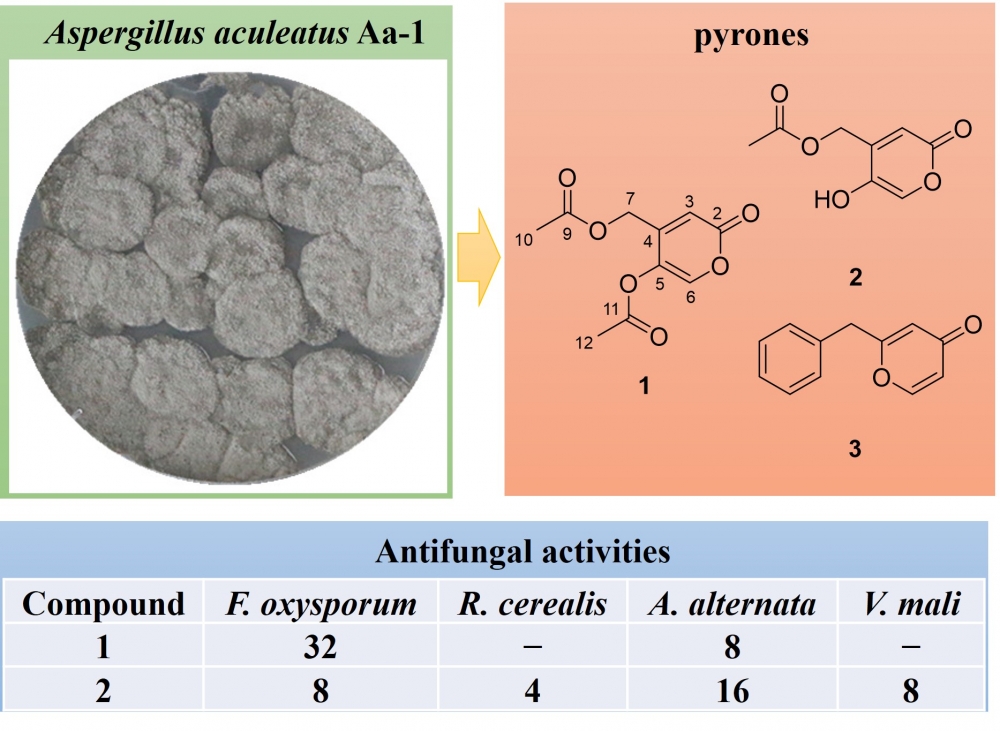
This paper presents a chemical study of the tobacco-derived fungus Aspergillus aculeatus Aa-1. Three pyrones including a new α-pyrone namely asperacuone A (1), the α-pyrone saadamycin (2), and the 2-benzyl-γ-pyrone (3) were isolated from the EtOAc extract of this fungal strain. The chemical structures of these compounds were precisely determined via nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1D/2D NMR) as well as high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HRESIMS). The antifungal activities of compounds 1–3 were then evaluated against six agricultural pathogenic fungi. While compound 1 revealed strong inhibitory potency against Alternaria alternata (minimum inhibitory concentration [MIC] = 8 μg/mL), compound 2 showed broad-spectrum inhibitory activities against the tested pathogens (MIC = 4–16 μg/mL)
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2511.3719 Keywords Tobacco-derived fungus Aspergillus aculeatus secondary metabolite α-pyrone antifungal activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Nicocembranoside A: A new neuroprotective cembrane glycoside from Nicotiana tabacum L.
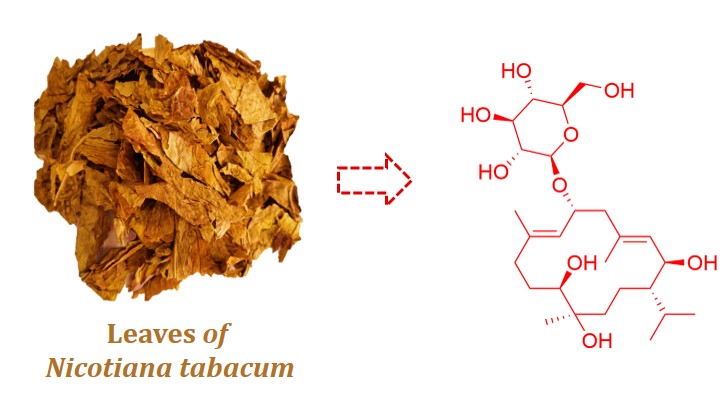
Cembrane-type diterpenoids are recognized for their medicinal significance.The phytochemical investigation of Nicotiana tabacum L. led to the isolation of Nicocembranoside A (1), a novel cembrane glycoside, represents the ninth naturally occurring cembrane glycoside and the first isolated from N. tabacum leaves. The structure of 1 was elucidated through comprehensive spectroscopic analyses, including 1D (1H, 13C NMR) and 2D NMR (COSY, HSQC, HMBC, ROESY), complemented by HRESIMS and biosynthetic precedence. Additionally, seven known compounds were also isolated and characterized. Preliminary evaluation demonstrated 1 exhibits neuroprotective effect against glutamate-induced cytotoxicity
in PC12 cells at 10 μM.
Two new compounds from the leaves of Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl

A new phenanthrene derivative and a new phenylethanoid glycoside were isolated from Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl leaves, named as 5,6-dimethoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene- 1,2,7-triol (1), phenethyl alcohol 8-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→3)-O-β-D- glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (2). These structures were determined by analysing their physical and chemical properties and using high-resolution mass spectrometry, infrared spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance and other spectroscopic techniques. In addition, the toxic activity of the isolated compounds on RAW 264.7 cells was evaluated, but the isolated compounds did not show significant activity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2511.3726 Keywords Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl phenylethanoid glycoside phenanthrene derivative DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Penioxalone A: A new isocoumarine derivative fromPenicillium oxalicum with potent cytotoxic effects on A549 cells

A chemical analysis of Penicillium oxalicum, a fungus isolated from saline soil, resulted in the discovery of four bioactive compounds (1–4), including a new resorcylic acid lactone, named penioxalone A (1). The structural characterization of penioxalone A was achieved through comprehensive spectroscopic techniques, including 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy, coupled with HRESIMS data. To determine its absolute configuration, experimental data from ECD and ORD were compared with theoretical calculations. The cytotoxicity of compounds 1, 3, and 4 was assessed against A549 human lung carcinoma cells, revealing IC₅₀ values of 3.6, 0.23, and 0.35 μM, respectively. These compounds exhibited enhanced potency compared to cisplatin, a standard chemotherapy drug, which had an IC₅₀ of 4.2 μM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2511.3716 Keywords Fungus Penicillium oxalicum penioxalone A resorcylic acid lactone cytotoxic activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
