JOURNAL 3648
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2026 Issue: 2
p.8 - 8
Viewed 30 times.
-
Quoctuan Nguyen

-
Sunhyeong Choi

-
Hongda Yun

-
Youngmi Lee

-
Chulmin Kim

-
Seojeong Oh

-
Mansoo Cho

-
Eunsol Lee

-
Jungwon Seo

-
Hyun Ju Jung

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
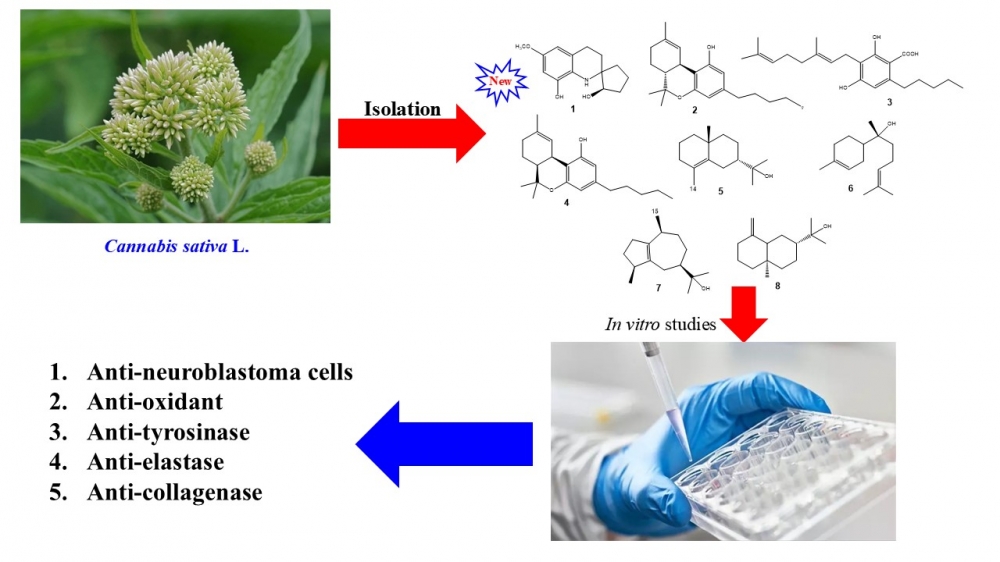
Cannabis sativa L. is a significant plant widely used for both medicinal and recreational purposes. Previous studies have reported that the secondary metabolites of this plant continue to play a crucial role in drug research and development. This study aims to investigate bioactive compounds in the n-hexane fraction obtained from the ethanolic extract of C. sativa flowers. The isolation yielded eight compounds (1-8), including one new compound (1). Their chemical structures were elucidated by 1D and 2D NMR, HR-ESI-MS, and comparisons with previously reported data. The results of the preliminary biological evaluation revealed that compounds 2-4 and 8 suppressed the proliferation of SK-N-SH cells at 10 μM. Notably, compound 4 displayed the strongest activity, with an IC50 value of 22.53 ± 1.92 μM, suggesting its potential as a candidate for the development of neuroblastoma cell proliferation inhibitors. In addition, compounds 1-8 were also evaluated for antioxidant, tyrosinase, elastase, and collagenase inhibitory activities. Among them, compound 1 showed the highest antioxidant activity, inhibiting 50.89% at 100 μM, compared with ascorbic acid. Compounds 1-3 and 6-8 also demonstrated elastase inhibitory activity, with inhibition rates ranking from 49.95% to 56.68% at 1 mM, relative to oleanic acid as a positive control. Similarly, compounds 1, 3, and 5 inhibited collagenase, with inhibition rates ranging from 55.34% to 73.17% relative to EGCG as a positive control. However, all compounds displayed relatively weak tyrosinase inhibitory effects, with inhibition ranging from 5.22% to 31.02%. This study also represents the first published evaluation of the inhibitory activities of isolated compounds from C. sativa flowers against tyrosinase, elastase, and collagenase.
KEYWORDS- Cannabis sativa
- cannabinoids
- SK-N-SH cells
- tyrosinase
- elastase
- collagenase