JOURNAL 2753
Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2023 Issue: 1 January-June
p.114 - 127
Viewed 2154 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
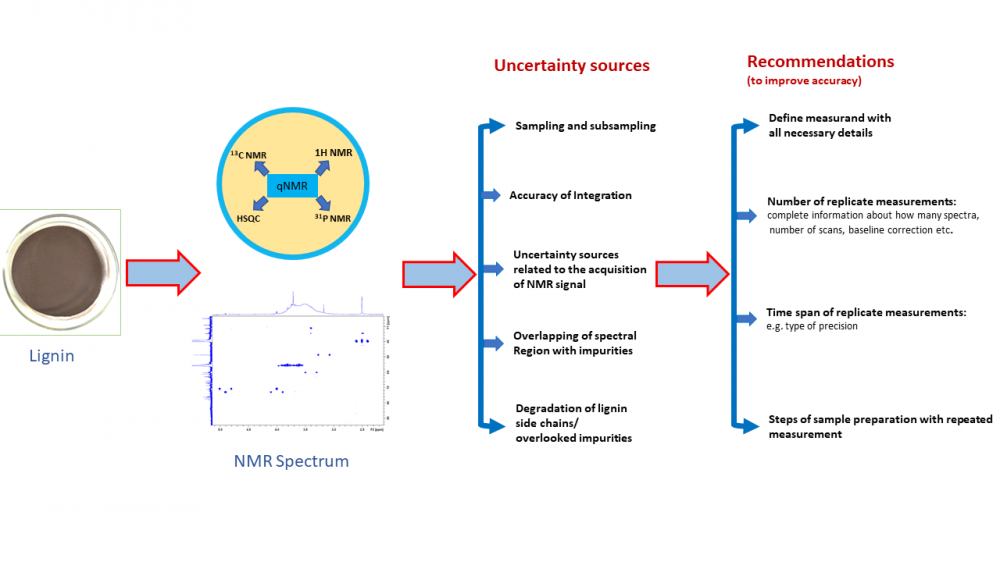
ABSTRACT
Lignin analysis using quantitative NMR (qNMR) has received a lot of attention recently and has been the topic of a large number of papers. The large majority of them report high-quality research. However, when trying to understand what is the accuracy that can be achieved with such analysis and which of the approaches are more accurate, it turns out that it is difficult to impossible to compare the accuracy of the methods. The main reasons are that different authors use (1) different types of lignin, (2) different measurands and (3) different ways of presenting precision and trueness data. Precision is mostly presented as standard deviation between replicate measurement results but it is in most cases not specified whether the precision relates to repeatability, intermediate precision or some other precision type. Bias is typically termed as “error” and usually expressed as difference from a reference value obtained from an artificial model system or difference from results of independent measurements. Again, insufficient detail is often given. Accuracy in terms of “measurement uncertainty” is hardly ever presented. Some uncertainty sources, most notably variability between subsamples of the same bulk of lignin, are only seldom addressed. We present an analysis of the situation on the basis of 21 papers and give some recommendations for future workers in the field. We hope that this work will be useful for researchers using qNMR for the analysis of lignin, as well as using qNMR for the analysis of natural products more generally.
KEYWORDS- Lignin
- Precision
- Bias
- Accuracy
- NMR
- qNMR