JOURNAL 3380
Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2024 Issue: 2 July-December
p.146 - 164
Viewed 1310 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
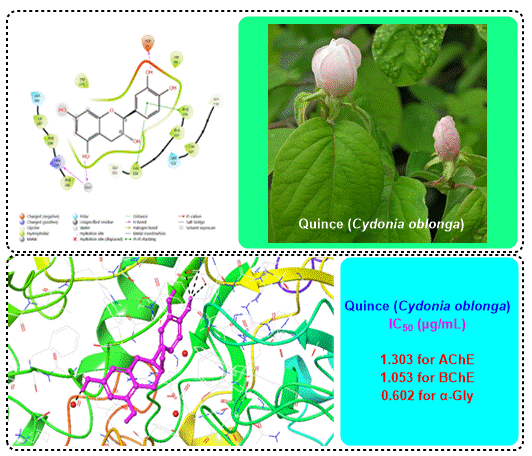
In this study, quantification of secondary metabolites of Cydonia oblonga (Quince) leaves by LC-MS/MS and antioxidant, cholinergic and α-Glycosidase activities were reported. LC-MS/MS analyses of the studied extract showed that the highest phenolic constituents of species were catechin (2024.9 ± 80.9 μg/L), vanillic acid (1121.8 ± 39.3 μg/L) and fumaric acid (486.7 ± 16.5 μg/L). The ethanol extract of quince leaves inhibited the α-glycosidase enzyme with an IC50: 0.6 μg/mL value. In order to determine the anti-Alzheimer activity of the plant extract, inhibition studies were carried out on acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) enzymes. The IC50 values of the plant extract were found to be 1.3 μg/mL for AChE and 1.5 μg/mL for BChE. In addition, free radical scavenging and metal reduction tests were performed to determine the antioxidant activity of the plant and the results were compared with Trolox. It was understood that the antioxidant potential of the plant was lower than Trolox. The results from biological abilities, molecular docking of catechin hydrate as abundant phenolic compounds in quince leaves extract to be an inhibitor candidate for AChE, BChE and α-glycosidase.
KEYWORDS- Quince
- enzyme inhibition
- antioxidant
- Alzheimer’s disease
- molecular docking
- polyphenol content.