JOURNAL 3093
Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Year: 2024 Issue: 3 Special Issue: Abstracts 3rd. TCS, International Food Chemistry Congress February 29-March 03,2024 Antalya Türkiye
p.68 - 68
Viewed 1209 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
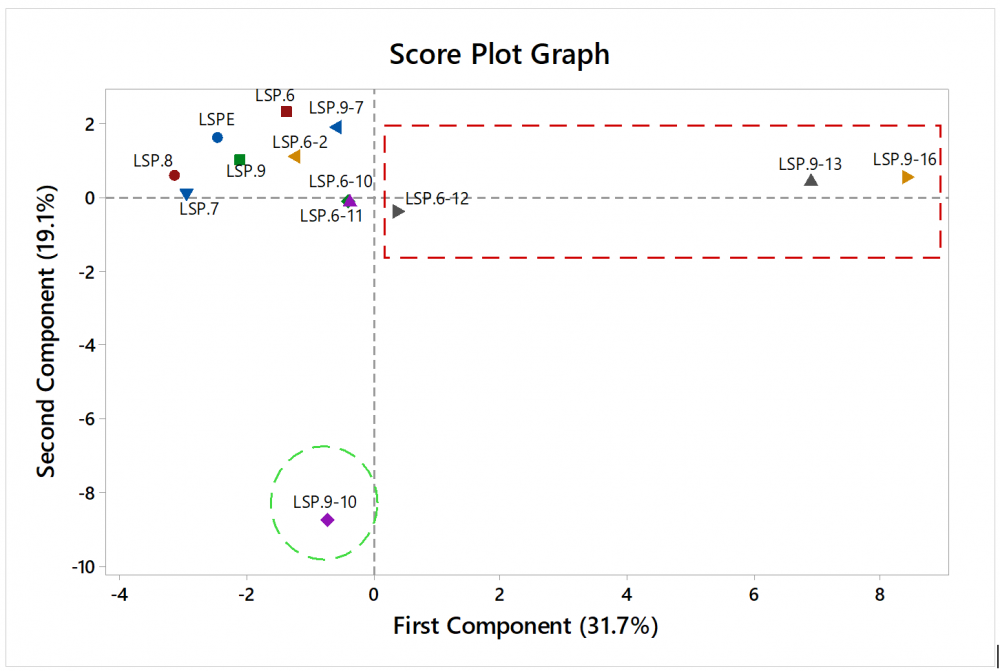
Mushrooms have become increasingly important in human nutrition due to their nutritional, pharmacological, and organoleptic properties [1]. Edible mushrooms are rich in minerals and have high water, protein, fiber, and carbohydrate content as well as low fat/energy levels, making them an excellent food for low-calorie diets [1]. Therefore, mushrooms are valuable foods because of their content. People prefer wild edible mushrooms for their aroma content and valuable nutrients, including unsaturated fatty acids, fibers, carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, and minerals [2,3]. Mushrooms are well-researched for their chemical composition and biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antiviral, antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-hypercholesterolemia, anti-hypertension, and immunomodulatory activities [1,4,5]. Fungi have attracted a great deal of attention in the last two decades, as many of them show cytotoxic activity and play an important role in the treatment of diseases such as cancer [5]. The aim of this study was to investigate the cytotoxic activity of petroleum ether extracts of Lactarius salmonicolor against colon (CaCo-2), lung (H1299), human breast (MCF-7) cancer cell lines, and kidney (HEK293) healthy cell lines by MTT assay and to determine cytotoxic ingredients using GC-MS and chemometrics. Subsequently, activity-guided fractionation was performed with the support of GC-MS elucidation. The percentage amounts of 36 common compounds elucidated from one extract, four fractions, eight sub-fractions, and their cytotoxic activity data against four cancer cell lines were subjected to Principal Component Analysis to reveal the cytotoxic compounds responsible for the total cytotoxic activity. The score and loading graphs of PCA monitored the cytotoxic compounds. In conclusion, the cytotoxic activity of the extract is due to the presence of azelaic acid, serine, sterols, and desmosterol, as well as the fatty acids, particularly long-chain fatty acids. In other words, the cytotoxic activity may be due to its polyunsaturated fatty acids and steroidal compounds.
KEYWORDS- Lactarius salmonicolor
- edible mushroom
- cytotoxic activity
- GC-MS
- steroids
- principal component analysis (PCA).