JOURNAL 1270
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2020 Issue: 2 March-April
p.116 - 128
Viewed 5887 times.
-
Yoon Hee Kim

-
So Mi Kim

-
Jae Kyoung Lee

-
Sung Kwan Jo

-
Hyung Joong Kim

-
Kyu Min Cha

-
Cho Young Lim

-
Joo Myung Moon

-
Tae Young Kim

-
Eun Ji Kim

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
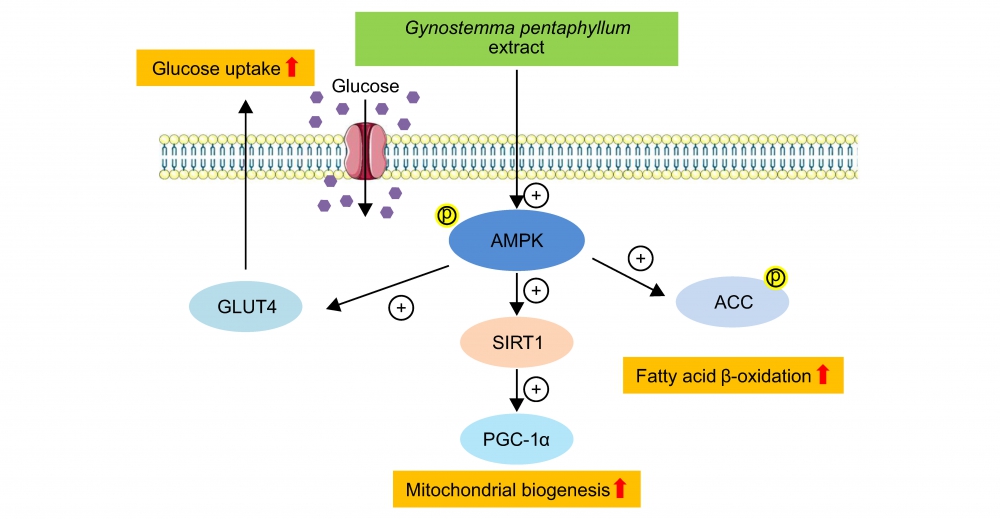
In the present study, we investigated a saponin-enriched fraction from Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract (GPE) and isolated gypenoside L (GL), gypenoside LI (GLI), and ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3). To explore the anti-obesity activities of these compounds, we investigated the effects of GL, GLI, and Rg3 on glucose uptake and activation of AMPK in L6 skeletal muscle cells. GPE, GL, GLI, and Rg3 markedly increased glucose uptake activity and GLUT4 gene expression in L6 myotubes. The enhanced glucose uptake was mediated by the activation of the AMPK-ACC signaling pathway. In addition, we observed that GPE, GL, GLI, and Rg3 increased the expression of SIRT1 and PPARγ coacvtivator-1α (PGC-1α). Our results suggest the potential use of Gynostemma pentaphyllum in developing a therapeutic agent to reduce body weight and prevent diet-related diseases via glucose uptake and AMPK activation.
KEYWORDS- Gynostemma pentaphyllum
- gypenosides
- L6 skeletal muscle cells
- glucose uptake
- AMPK
- SIRT1