JOURNAL 1728
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2021 Issue: 2 March-April
p.130 - 135
Viewed 3201 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
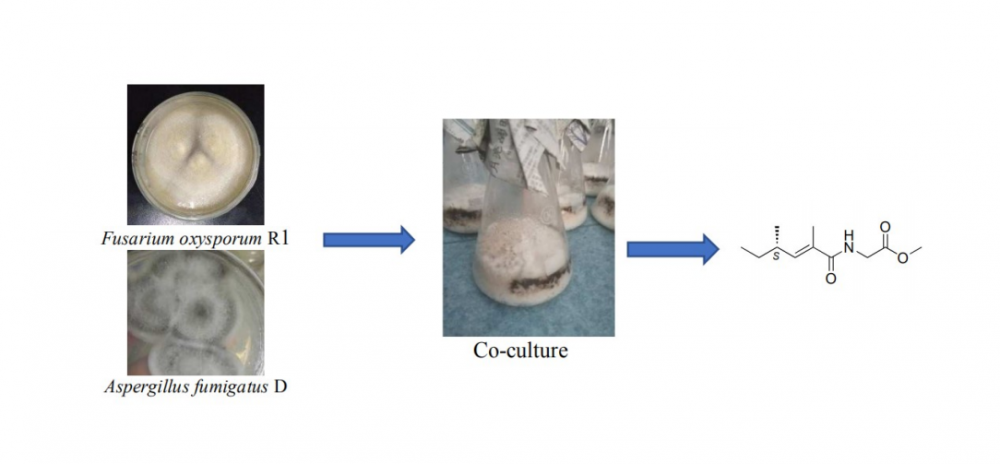
ABSTRACT
Chemical investigation of a co-culture of two endophytic fungi Aspergillus fumigatus D and Fusarium oxysporum R1 from two traditional medicinal plants, Edgeworthia chrysantha Lindl. and Rumex madaio Makino, led to isolation of a new amide 1 and six known compounds, including neovasinin (2), neovasifuranone B (3), N-(2-phenylethyl)acetamide (4), α-linolenic acid (5), α-elaeostearic acid (6), palmitoleic acid (7). On the basis of extensive spectroscopic analysis including 1D and 2D NMR, HR-ESI-MS and optical rotation measurement as well as comparison of literature data, chemical structure of 1 was unambiguous elucidated as (S, E)-methyl-2-(2,4-dimethylhex-2-enamido)acetate. Bioassay results indicated that none of these compounds exhibited strong inhibitory effect on three human pathogens Escherichia coli, Staphyloccocus aureus and Candida albicans with MIC values of ≥25 μM.
KEYWORDS- Endophytic fungus
- Aspergillus fumigatus D
- Fusarium oxysporum R1
- co-culture
- amide
- antimicrobial effect