JOURNAL 2161
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Issue: 4 July-August
p.387 - 392
Viewed 2885 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
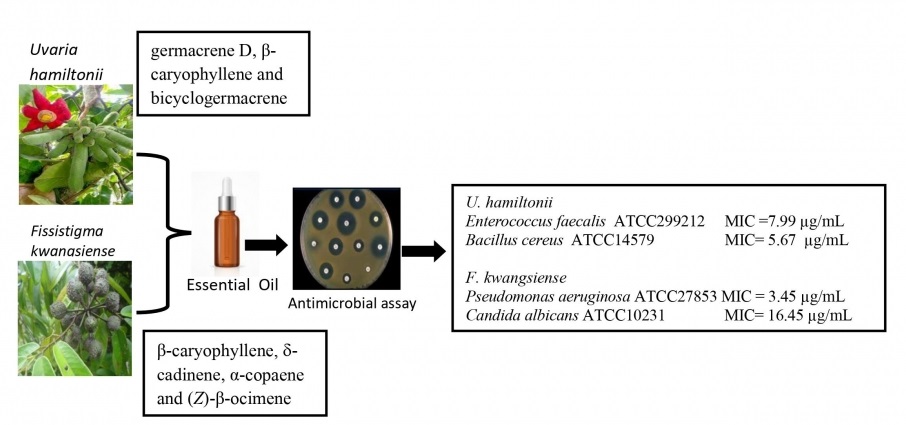
ABSTRACT
In this study, essential oils hydrodistilled from the leaves of Uvaria hamiltonii Hook. f. & Thoms. and Fissistigma kwangsiensis Tsiang & P. T. Li (Annonaceae) collected in Vietnam were analyzed by gas chromatographic techniques, and screened for the antimicrobial activities. The composition of both essential oils was dominated by sesquiterpenoids (70.0% and 78.7%, respectively). The main constituents of U. hamiltonii were germacrene D (22.9%), β-caryophyllene (21.1%), bicyclogermacrene (11.2%) and caryophyllene oxide (8.6%). The essential oil of F. kwangsiensis also showed abundant sesquiterpenes β-caryophyllene (24.5%), d-cadinene (13.4%) and α-copaene (5.6%), but also included (Z)-β-ocimene (6.7%). The leaf oil of U. hamiltonii demonstrated notable antimicrobial activity against Enterococcus faecalis ATCC299212 with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value of 7.99 µg/mL and Bacillus cereus ATCC14579 (MIC 5.67 µg/mL) while F. kwangsiensis showed the most potent activity towards Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC27853 and Candida albicans ATCC10231, with MIC values of 3.45 µg/mL and 16.45 µg/mL, respectively. Both essential oils should be considered for further investigation as renewable “green” antimicrobial agents.
KEYWORDS- Antimicrobial activity
- essential oil composition
- sesquiterpenes