JOURNAL 2112
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Issue: 4 July-August
p.358 - 369
Viewed 2845 times.
-
Bunleu Sungthong

-
Kingkaeo Sithon

-
Panyada Panyatip

-
Sarin Tadtong

-
Nadtanet Nunthaboot

-
Ploenthip Puthongking

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
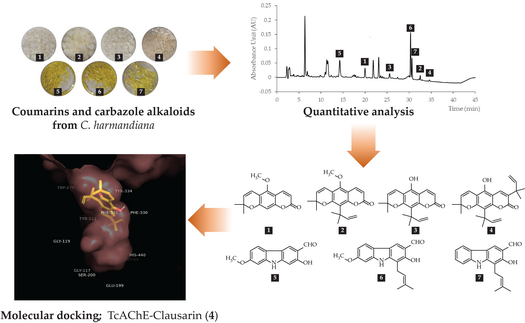
Coumarins and carbazole alkaloids are natural compounds, often with neurological properties, especially as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. In order to screen the candidate anti-acetylcholinesterase agents, in-silico molecular docking was performed aiming to predict the binding mechanism and the results were used to identify pharmacophores of coumarins and carbazole alkaloids from Clausena harmandiana as AChE inhibitory activity. All isolated compounds are xanthoxyletin (1), dentatin (2), nordentatin (3), clausarin (4), 7-methoxymukonal (5), 7-methoxyheptaphylline (6) and heptaphylline (7) displayed the stable binding interactions with Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase (TcAChE) enzyme via π-π interactions, hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions. All compounds exhibited the interaction with the peripheral anionic site of TcAChE same manner of standard anti-alzheimer drugs. ADME prediction revealed that all compounds met the requirement of drug likeness of Lipinski’s rule of five and had high CNS absorption, excepted 4 should be structure modification to improve CNS penetration. Besides 4, 6 and 7 displayed the highest acetylcholinesterase inhibitor activity among the other compounds. Interestingly, 6 had a high yield (58.01 mg/g extract) from C. harmandiana. It should be a candidate as an anti-acetylcholinesterase inhibitor agent.
KEYWORDS- Clausena harmandiana
- molecular docking
- coumarins
- carbazole alkaloids
- Alzheimer’s disease
- ADME