JOURNAL 2547
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2023 Issue: 3 May-June
p.571 - 576
Viewed 3384 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
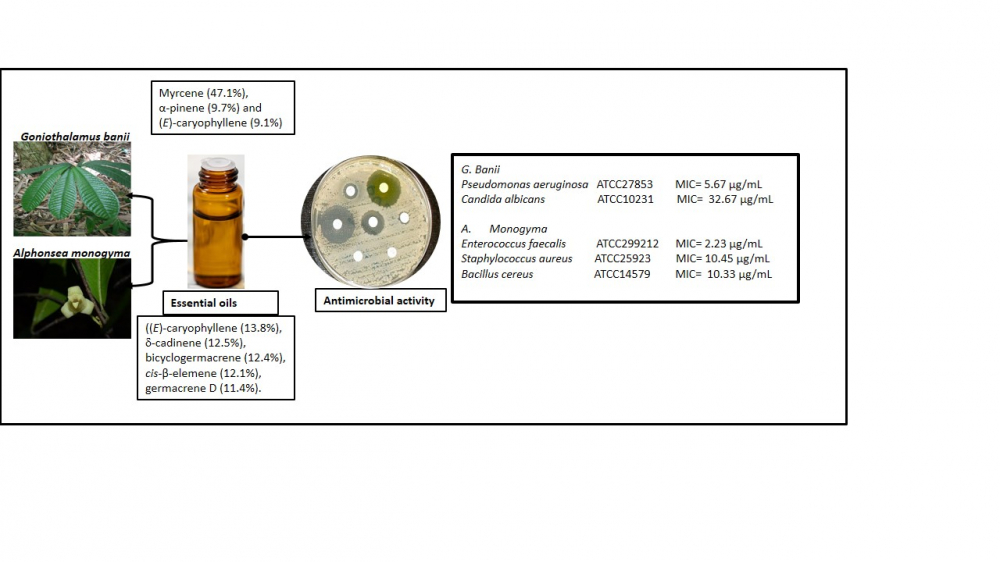
Essential oils from the leaves of Alphonsea monogyma Merr. & Chun and Goniothalamus banii B. H. Quang, R. K. Choudhary & V.T. Chinh from Vietnam were obtained by hydrodisitllation and the chemical components determined by gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC/MS). Also the microdilution broth assay was used to test the antimicrobial activity of the essential oils. The respective yields of the essential oils were 0.18% (v/w) and 0.355% (v/w), respectively. The major components of A. monogyma were (E)-caryophyllene (13.8%), d-cadinene (12.5%), bicyclogermacrene (12.4%), cis-β-elemene (12.1%), and germacrene D (11.4%). However, myrcene (47.1%), α-pinene (9.7%) and (E)-caryophyllene (9.1%) were the dominant constituents of the essential oil of G. banii. The leaf essential oil of A. monogyma displayed potent antimicrobial activity towards the Gram-positive microorganisms of Enterococcus faecalis ATCC299212, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC25923 and Bacillus cereus ATCC14579 with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of 2.23 µg/mL, 10.45 µg/mL and 10.33 µg/mL, respectively. On the other hand, essential oil from G. banii exhibited the most effective antibacterial against Gram-negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC27853 (MIC 5.67 µg/mL), and anti-candidal action towards Candida albicans ATCC10231 (MIC 32.67 µg/mL). The chemical constituents and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils of A. monogyma and G. banii were being reported for the first time.
KEYWORDS- Alphonsea monogyma
- essential oil composition
- terpenes
- antimicrobial activity
- anti-candidal activity