JOURNAL 2627
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2023 Issue: 4 July-August
p.595 - 614
Viewed 3847 times.
-
Abbas Ali

-
Nurhayat Tabanca

-
Vijayasankar Raman

-
Cristina Avanto

-
Xiangbing Yang

-
Betül Demirci

-
Amar Chittiboyina

-
Ikhlas A. Khan

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
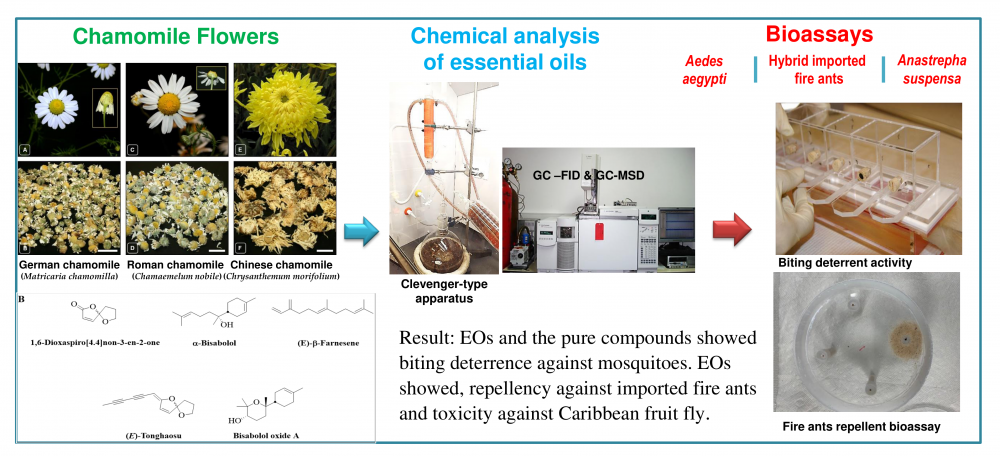
ABSTRACT
In this study, the essential oils (EOs) of flowers from German chamomile (GCEOs 1-5) Matricaria chamomilla L., Roman chamomile (RCEOs 1-2) Chamaemelum nobile (L.) All, and Chinese chamomile (CCEO-1) or “Juhua” Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat were characterized by GC-FID and GC-MS analysis. EOs were tested for biting deterrence/repellency against Aedes aegypti and hybrid imported fire ants and for toxicity against Anastrepha suspensa. GCEOs 1-5 were characterized by the higher contents of α-bisabolol oxide A (43%-66%) and α-bisabolol oxide B (10%-16%) whereas isobutyl angelate (16%-17%), 2-butenyl angelate (12%-13%), isoamyl tiglate (11%-12%), 3-methyl pentylangelate (8%-11%), and trans-pinocarveol (6%-7%) were major compounds of RCEOs 1 and 2. The CCEO-1 was rich in borneol (31%), ar-curcumene (12%), bornyl acetate (7%) and intermedeol (5%). Biting deterrence of GCEO-2 and -3, and CCEO-1 was similar to N,N-diethyl-3-methylbenzamide (DEET) whereas the activity of the other EOs was lower than DEET against Ae. aegypti. The activity of pure compounds α-bisabolol and 1,6-dioxaspiro[4.4]non-3-en-2-one from German chamomiles was also similar to DEET against Ae. aegypti. Repellency of German chamomile EO, GCEO-F against hybrid imported fire ants was higher whereas the activity of Roman chamomile EO, RCEO-PT was lower than DEET. All EOs, GCEO-4, RCEO-2, and CCEO-1 were toxic against female A. suspensa. Further research using intensive in vivo bioassays will be conducted to explore the potential of these natural products in insect pest management strategies.
KEYWORDS- Chamomile essential oils
- α-bisabolol
- repellency
- imported fire ant
- fruit fly
- mosquitoes