JOURNAL 2720
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2023 Issue: 5 September-October
p.878 - 895
Viewed 2561 times.
-
Elizabeth Quintero-Rueda

-
Sindi A Velandia

-
Raquel E Ocazionez

-
Elena E Stashenko

-
Paola Rondón-Villarreal

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
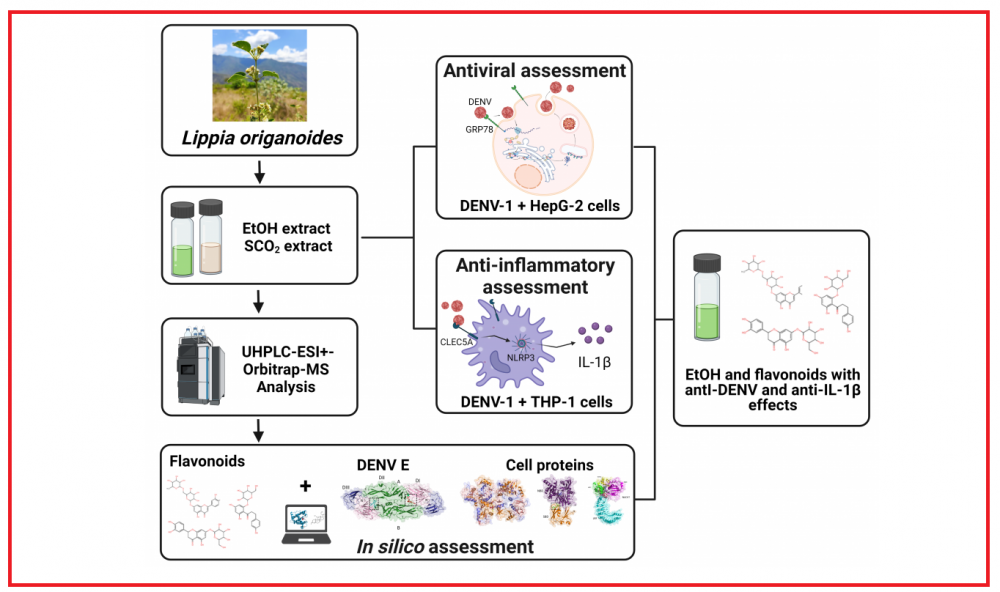
ABSTRACT
Despite intense research efforts, no approved effective therapies are available for dengue treatment. Standardized plant extracts could serve as potential candidates for developing plant-based treatments for dengue. We have compared the anti-dengue potential of ethanolic (EtOH) and supercritical (SCO2) extracts of Lippia origanoides Kunth (Verbenacea). The mode of antiviral action and the effect on the release of IL-β from DENV-1-stimulated macrophages (PMA/THP-1) were evaluated. In silico analyses were performed to predict molecular interactions between flavonoids identified in the UHPLC–ESI+–Orbitrap–MS analysis and target proteins. The EtOH extract showed a strong antiviral effect (IC50, 22 and 17 µg/mL; SI, 20 and 23) before and during DENV-1 adsorption to liver (HepG-2) cells. SCO2 showed a weak antiviral effect. EtOH, but not SCO2, reduced the level of IL-1β released from PMA/THP-1 cells by 45-55%. Flavonoid glycosides were identified in EtOH but not in SCO2. Seventeen flavonoids were predicted to bind to DENV E, GRP78, CLEC5A, and NLRP3 proteins involved in DENV replication and IL-1β production. The data provide a first step towards defining the potential of L. origanoides extract as a candidate for developing phytotherapeutics for dengue.
KEYWORDS- Plant extracts
- Lippia origanoides
- dengue
- dengue virus
- macrophages
- cytokine