JOURNAL 3314
Records of Natural Products
Available Online: October 26,2024
p.1 - 6
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.481.24.08.3314 (DOI number will be activated after the manuscript has been available in an issue.)
Viewed 47 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
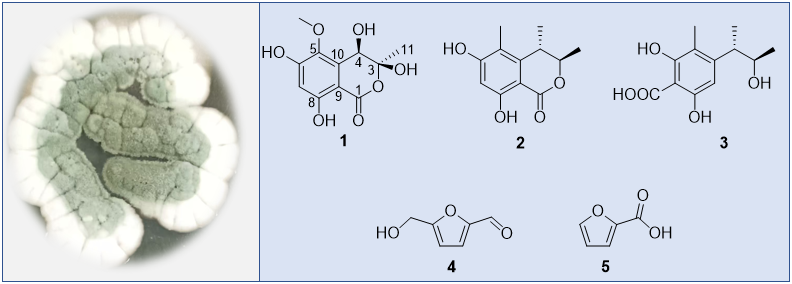
ABSTRACT
Penicillium is a significant source of bioactive compounds, with the well-known antibiotics penicillin and griseofulvin derived from P. chrysogenum and P. griseofulvum, respectively. In our study, the fungus Penicillium sp. was isolated from shallow-sea sediments. The ethyl acetate extract of this strain exhibited moderate inhibitory effects against Escherichia coli. Subsequent isolation and purification of the extract led to the identification of five compounds (1-5), including a new highly oxygenated isocoumarin and two analogues (2 and 3), as well as two furan derivatives (4 and 5). The structure determination of compound 1 was conducted by extensive analysis of spectroscopic data, including 1H and 13C NMR, as well as 2D NMR techniques (HSQC, COSY, HMBC, and NOESY), in addition to HRESIMS. The known compounds 2-4 were identified as decarboxydihydrocitrinone (2), phenol A acid (3), 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural (4), 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furancarboxaldehyde (5) by comparing their 1H and 13C NMR data with those reported in the literature. compound 1 exhibited an MIC value of 64 mg/mL toward Escherichia coli.
KEYWORDS- Penicillium sp.
- isocoumarin
- fungus
- isolation
- structure elucidation