JOURNAL 1483
Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Reports
Year: 2019 Issue: 1-2 (January-December)
p.24 - 31
Viewed 3711 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
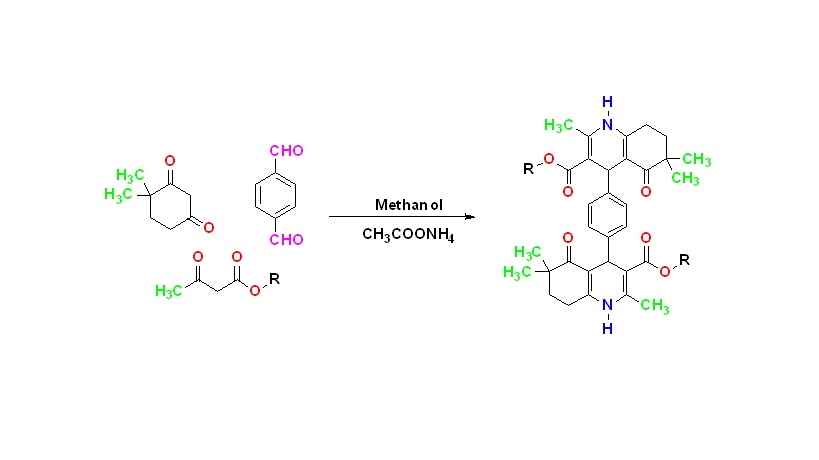
ABSTRACT
It is known that microorganisms develop resistance to the drugs used in the treatment of diseases caused by bacteria and fungi. Therefore, the discovery of new drug molecules have great importance for the treatment of these diseases. In this study, compounds having dialkyl 4,4'-(1,4-phenylene)bis(2,6,6-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate) general structure which are expected to exhibit antibacterial and antifungal activity were synthesized. 1H-NMR and IR analyzes were performed to prove their structures. All compounds were tested against Gram (+) Staphylococcus aureus and Gram (-) Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa to evaluate their in vitro antibacterial activity; Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii to evaluate in vitro antifungal activity. According to the biological activity data, the most active derivative in the series was compound 2 as an antibacterial agent and compound 7 as an antifungal agent.
KEYWORDS- hexahydroquinoline
- Hantzsch synthesis
- antibacterial
- antifungal
- inhibition