Journal of Chemical Metrology
A scientific open access journal in the field of analytical chemistry and accreditationLATEST ARTICLES
Desorption of ethanol from internal surface of the cylinders
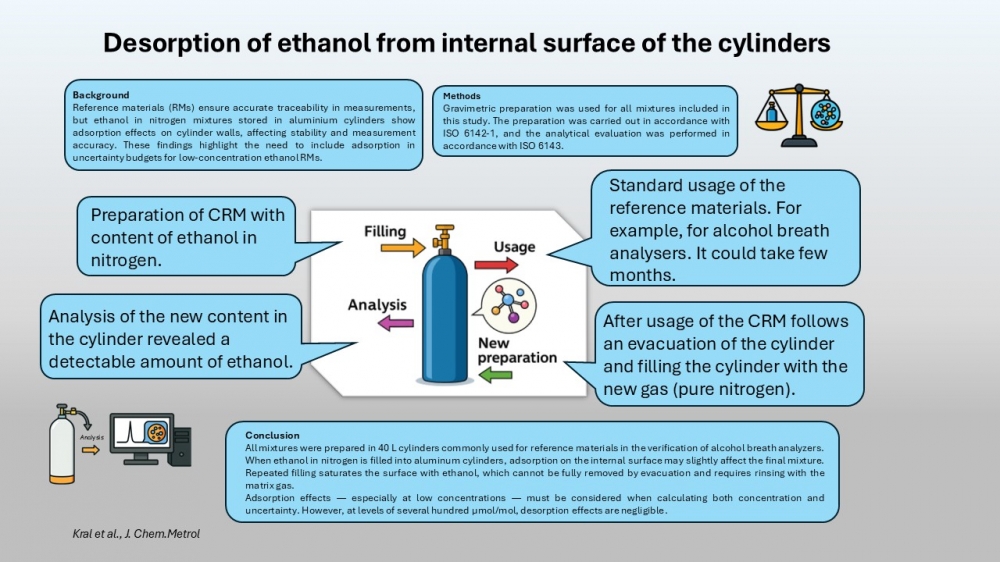
Reference materials (RMs) are essential for ensuring metrological traceability in various fields, including environmental monitoring, chemical analysis, and the verification of alcohol breath analyzers. One critical property of RMs is their long-term stability, particularly for gas mixtures such as ethanol in nitrogen, which are stored in pressurized aluminum cylinders. This paper describes the preparation of such gas mixtures according to ISO 6142-1, utilizing differential weighing to minimize the influence of ambient conditions and ensure accurate composition. The effects of adsorption of ethanol on the internal surfaces of aluminum cylinders were experimentally investigated. Results indicate that ethanol can remain adsorbed on the cylinder walls even after evacuation, leading to measurable ethanol concentrations upon subsequent refilling with nitrogen. Repeated fillings demonstrated a decrease in ethanol levels, confirming the saturation and gradual desorption behavior. These findings underscore the necessity to consider adsorption effects in the uncertainty budget and composition calculations for low-concentration ethanol-in-nitrogen RMs.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.121.2507.3596 Keywords Stability reference materials ethanol pressurized cylinders gas chromatography desorption DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Development of a quality control material for conductivity measurements in food and environmental applications
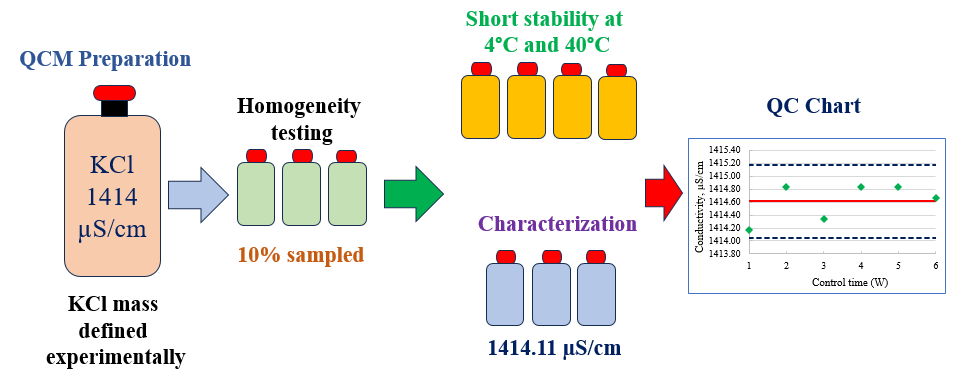
The accuracy and reliability of conductivity measurements in analytical laboratories depend significantly on the availability of quality control materials. This study addresses the preparation, homogeneity, stability and characterization of a potassium chloride (KCl) quality control material (QCM) of 1414 µS/cm based on ISO/TR 33402. OIML R-56 does not contain this conductivity value as a secondary standard, so the mass of KCl required to prepare such a solution was experimentally defined. The conductivity measurements were carried out at 25 °C using a conductivity meter calibrated by a CRM produced by the the Slovak Institute of Metrology (SMU), a signatory to the mutual recognition arrangement (MRA) of the International Committee of Weights and Measures (CIPM). The homogeneity study was carried out in accordance with ISO 33405 using 10% of the batch bottles and the analysis of variance (ANOVA) showed that the QCM batch is homogeneous. The short-term stability was carried out over 4 weeks storage time at 4°C and 40°C and the isochronous measurements showed no significant deviations over time. The characterization of the QCM along three days showed that, its conductivity was 1414.11 µS/cm. The uncertainty associated with the conductivity measurements was assessed based on the requirements of the Guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement (ISO GUM) and the EURACHEM/CITAC Guide, CG4 (Quantifying uncertainty in analytical measurement). It was found to be 23.10 µS/cm or 1.63%. A control chart was developed using the prepared QCM and the measured values remained within the control limits over the control time of six weeks. The prepared KCl QCM will be useful for use in quality control and instrumental validation in food, drug and environmental conductivity testing.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.119.2508.3607 Keywords Conductivity QCM ISO/TR 33402 homogeneity stability control chart DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Determination of phenolic content of Hypericum aucheri Jaub. & Spach by LC-HRMS and its antioxidant capacity
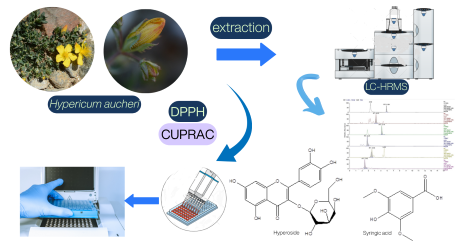
The study aims to identify the secondary metabolites of Hypericum aucheri Jaub. & Spach extracts using liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) and to evaluate the plant's antioxidant activity. Antioxidant activity was assessed using DPPH free radical scavenging and CUPRAC assays. The primary secondary metabolite detected was hyperoside, with concentrations of 1059.53 mg/L in acetone (Ac) extract and 389.73 mg/L in methanol (MeOH) extract. Sinapinic acid was the predominant compound in the chloroform (C) extract, with a concentration of 6646.53 mg/L. In addition, Ac extract showed the highest DPPH free radical scavenging activity (85.90±0.26 - 61.19±0.47%) of all the extracts tested. The MeOH extract exhibited the highest value in the CUPRAC assay (2.53±0.05 mmol TR g-1). The study highlights a numerical relationship between phenolic content and antioxidant activity, underscoring the importance of phenolics in their antioxidant functions.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.131.2512.3765 Keywords Hypericaceae Hypericum aucheri antioxidant LC-HRMS phenolic compounds DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.A New RP-HPLC method for stability indicating assay of pazopanib hydrochloride in tablet dosage form: method development, validation, and degradation kinetics
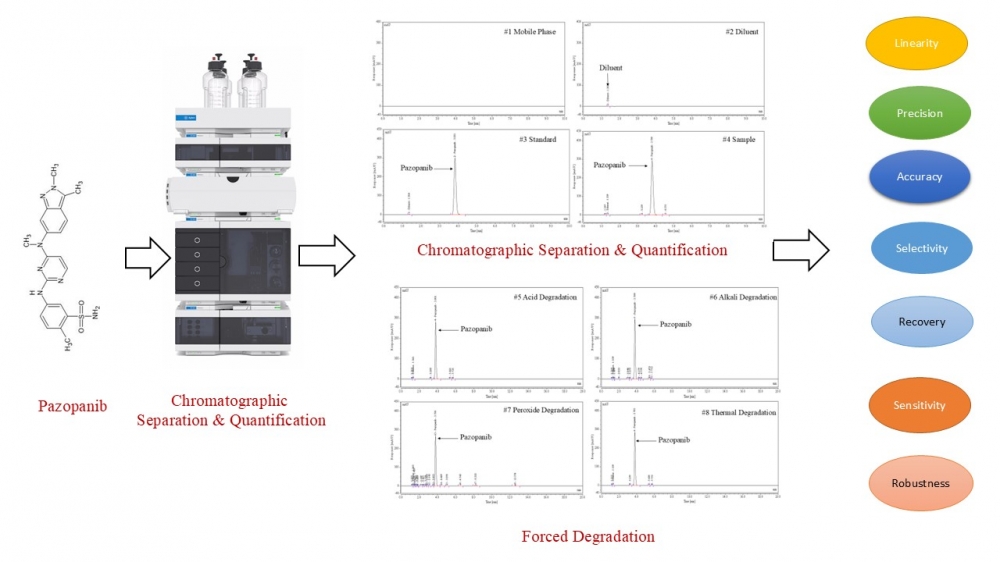
This study reports the development and validation of a novel, rapid, and stability-indicating reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) method for the quantification of pazopanib in tablet formulations. Chromatographic separation was achieved on an Inertsil ODS-3V column (150 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) using an isocratic mobile phase of 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid and acetonitrile (70:30, v/v) at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min with UV detection at 268 nm. The method demonstrated excellent resolution of pazopanib from its degradation products under forced degradation conditions, including acid/base hydrolysis, oxidation, photolysis, thermal, and humidity stress, confirming its stability-indicating capability. Validation in accordance with ICH Q2(R1) guidelines showed linearity over 25.71, 51.41, 82.26, 102.82, 123.38, and 154.23 µg/mL (r² > 0.999), precision with %RSD < 2.0, accuracy with recovery > 99%, and robustness under deliberate variations in chromatographic parameters. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) confirmed high sensitivity, and solution stability studies established analyte stability over 24 hours at 25 °C. With a runtime of 20 minutes and cost-efficient operation, this RP-HPLC method provides accurate, precise, and selective quantification of pazopanib in pharmaceutical dosage forms.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.130.2510.3711 Keywords Pazopanib hydrochloride stability indicating RP-HPLC method forced degradation study assay analytical method validation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.