Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
A scientific open access journal in the field of agricultural and food chemistry.LATEST ARTICLES
Comparative Evaluation of Phenolic Compounds of Flowers, Leaves and Stems of Wild Hypericum perforatum L. in Türkiye
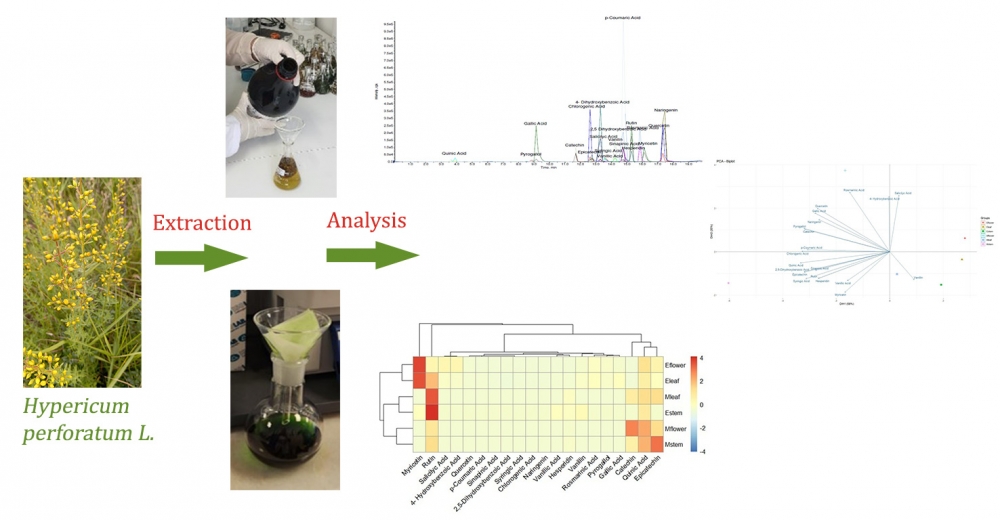
The phytochemical content of medicinal and aromatic plants is important for evaluating their biological activity and pharmacological efficacy. In this study, Hypericum perforatum L. (St. John's wort), a plant that grows naturally in many regions of Türkiye, was collected from the Çankırı (Eldivan) region, and the phenolic compounds of methanol and ethyl acetate extracts from the flower, leaf, and stem parts were investigated. Phenolic compounds were identified using LC-MS/MS. All analyses were performed in triplicate, and the results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. According to the findings, different parts of the same plant showed significant differences in phenolic compound content depending on the solvent used. In methanol extracts, quinic acid, catechin, epicatechin, and rutin were the compounds with the highest concentrations. The highest concentrations of quinic acid (12977.78 μg/g), catechin (5675.56 μg/g), epicatechin (18400 μg/g), and rutin (9244.44 μg/g) were determined in the methanol stem extract. In the study, the compound content identified in the methanol extract was higher than that in the ethyl acetate extract. However, the highest amounts of phenolic compounds were detected in the methanol stem extract among the methanol and ethyl acetate extracts. According to the LC-MS/MS results, methanolic extracts exhibited a higher phenolic compound content.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.43.2512.3756 Keywords Hypericum perforatum L St. Johns wort phenolic compounds LC-MS/MS Türkiye DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Nutrient Composition and Techno-functional Properties of Three Nigerian Spices and Sensory Acceptability of Traditional Dishes
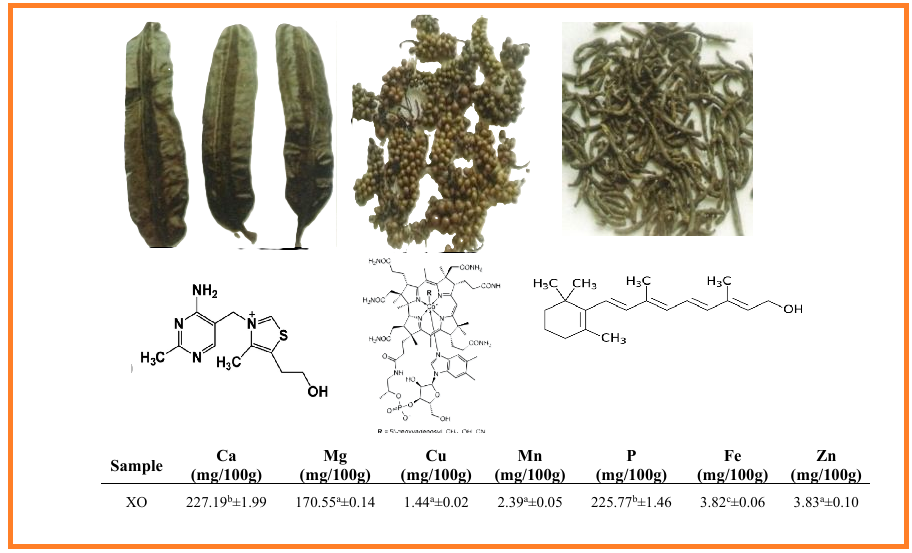
This study evaluated the functional and micronutrients in Piper guineense (uziza), Xylopia aethiopica (Guinea pepper) and Tetrapleura tetraptera (Aidan fruit) spices and also assessed the level of acceptability of the dishes prepared using these spices. The spices were processed before determining the functional, vitamin, mineral and sensory properties. The results show that the oil absorption capacity, foam and gelation capacities of the samples ranged from 1.94 – 2.39%, 13.56 – 10.78 g/mL and 8.45 – 6.00 g/mL respectively. Piper guineense was significantly higher in water absorption capacity (2.27%), bulk density (0.52 mg/100g) and swelling index (1.87 g/mL) while the least values were recorded in Tetrapleura tetraptera for water absorption capacity (2.14 g/mL) and swelling index (1.31 g/mL). Gelatinization temperature ranged between 58.73oC (Tetrapleura tetraptera) and 62.45oC (Xylopia aethiopica). Piper guineense was higher in Calcium (283.72 mg/100g), Phosphorus (249.96 mg/100g) and Iron (6.34 mg/100g). Tetrapleura tetraptera had the lowest values for Calcium (189.01 mg/100g), Magnesium (144.90 mg/100g), Copper (0.13 mg/100g), Manganese (0.84 mg/100g), Phosphorus (196.49 mg/100g) and Zinc (1.27 mg/100g), while sample Xylopia aethiopica had the least value for Fe (3.82 mg/100g) and higher values for Magnesium (170.55 mg/100g), Copper (1.44 mg/100g), Manganese (2.39 mg/100g) and Zinc (3.83 mg/100g). The vitamin B1 content of the samples ranged from 0.02 (Piper guineense) – 0.03 (Xylopia aethiopica and Tetrapleura tetraptera) mg/100g. The vitamin B2 content of samples ranged from 0.02 – 0.03 mg/100g. The vitamin B12 content of the samples ranged from 0.28 (Piper guineense) – 0.33 (Xylopia aethiopica) mg/100g. The vitamin C content of Piper guineense (1.84 mg/100g) was higher than other samples. The vitamins A and E contents ranged from 8.27 – 9.58 µg/100g and 0.85 – 1.72 mg/100g respectively. Tetrapleura tetraptera was highest while Xylopia aethiopica was the lowest. There were variations in the sensory score of the dishes prepared with theses spices.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.42.2511.3740 Keywords Spices Piper guineense Xylopia aethiopica sensory evaluation traditional Nigerian foods DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
Investigation of In Vitro Anti-diabetic Activity and Phenolic Component Profile of Mulberry Leaf Tinctures
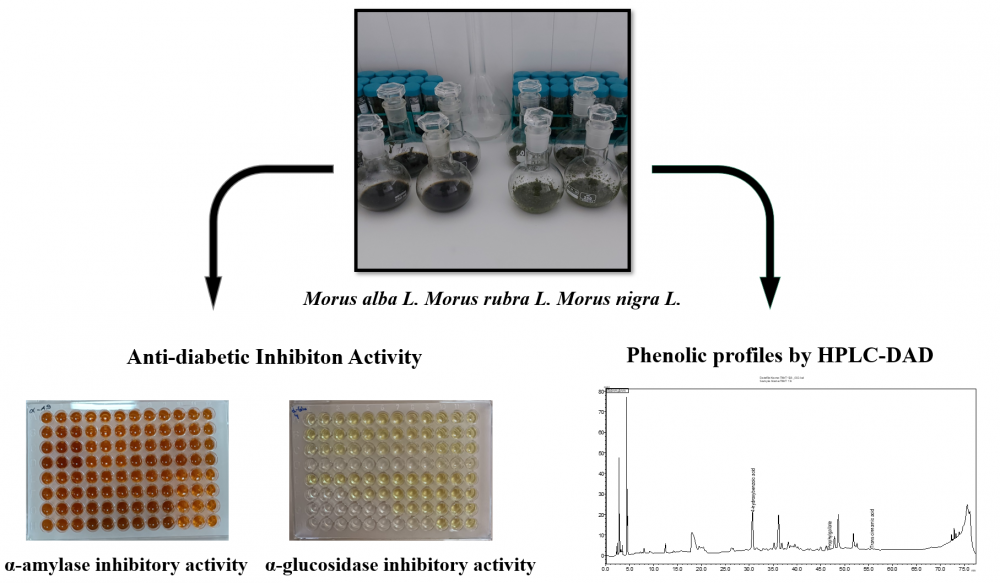
This study aimed to evaluate the in vitro anti-diabetic potential and phenolic compound profile of leaf tinctures prepared from fresh and dried leaves of three mulberry species (Morus alba L., Morus rubra L., and Morus nigra L.) using different plant-to-solvent ratios, with the objective of identifying the most effective formulation for Type II diabetes. For this purpose, ethanol:water (70:30, v/v) tinctures were prepared at 1:4, 1:5, 1:6, 1:7, and 1:8 (w/v) ratios, and their inhibitory activities against α-amylase and α-glucosidase enzymes were determined by a spectrophotometric method. Among all tested samples, the dried M. rubra L. leaf tincture prepared at a 1:6 ratio (TMrD 1:6) exhibited the strongest inhibitory activity, with IC₅₀ values of 24.11 μg/mL for α-amylase and 40.18 μg/mL for α-glucosidase. The phenolic compound profile of the most active tinctures was further investigated using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array detection (HPLC-DAD) through the screening of 42 phenolic compounds. Protocatechuic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, caffeic acid, and chlorogenic acid were quantitatively detected, whereas p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, coumarin, and trans-cinnamic acid were present only in trace amounts. Overall, the dried M. rubra L. leaf tincture (TMrD 1:6) demonstrated promising potential as a phytopharmaceutical candidate for diabetes management.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.41.2511.3728 Keywords Morus alba L. Morus rubra L. Morus nigra L. chemical profile anti-diyabetic activity tincture DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of Lomelosia rotata (M.Bieb.) Greuter & Burdet
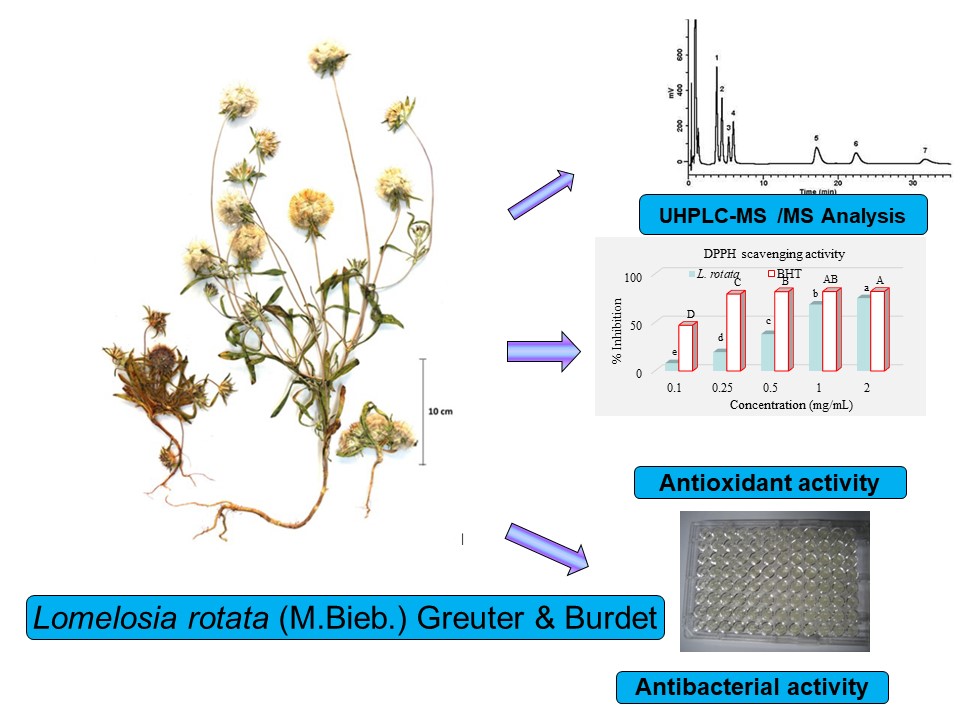
This study aimed to determine the phenolic compositions and biological activities of Lomelosia rotata (M.Bieb.) Greuter & Burdet (Caprifoliaceae). According to HPLC/MS-MS analysis results, quinic acid (253.058 mg/g) was detected as the primary component in L. rotata methanol extract. The total phenolic and total flavonoid contents of the extract were examined using the Folin-Ciocalteu reagent and aluminum chloride colorimetric assays, respectively. Phosphomolybdenum, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical-scavenging (DPPH), ferric-ion-reducing power (FRAP), and cupric-ion-reducing antioxidant activity (CUPRAC) methods were used to evaluate the antioxidant capacity. L. rotata methanolic extract showed an effective DPPH scavenging activity (IC50 = 23.30 μg/mL). Results showed that the extract had moderate reducing activity toward cupric and ferric ions. The methanol extract showed no antibacterial effect. Our study suggests that L. rotata extract has potential use as a natural antioxidant for food preservation and human health.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.40.2511.3722 Keywords Lomelosia rotata antibacterial activity antioxidant activity phenolics DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.