Records of Natural Products
A scientific open access journal in the field of natural products.LATEST ARTICLES
A mixture of potent polyphenolic anticarcinogens: Microarray analysis of their efficacy in MCF-7 and MCF-10A cell lines
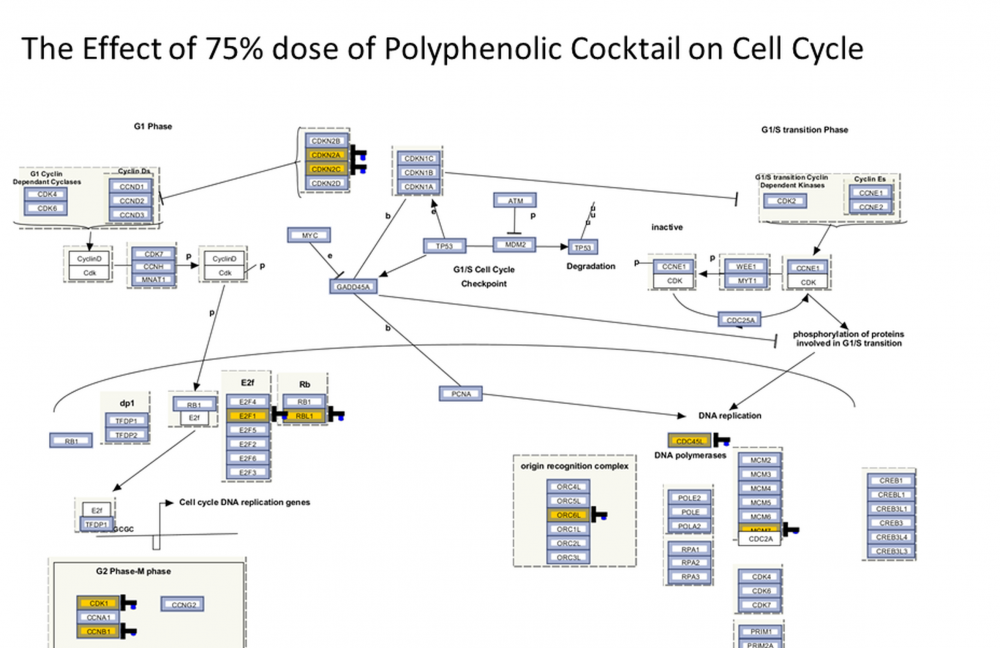
Polyphenols are abundantly available through diet and show great promise with their safe use against cancer. In our previous studies, we have shown cytotoxic effects of more than 30 polyphenols in breast cancer. In this study, we have aimed to investigate the effects of various polyphenols upon MCF-7 breast cancer and MCF-10A normal epithelial cells. To this end, we have designed a polyphenolic mixture based on the most effective concentrations of seven compounds, which is a first according to literature in terms of polyphenolic combination studies. Cell proliferation experiments were executed utilizing WST-1 and apoptotic status by Annexin V-PI. After determining most effective concentrations, we operated whole genome microarray analysis. Based on microarray data, the best effective concentration for both cell lines is 75% of polyphenolic mixture. In MCF-7 cell line, this dosage induced in down regulation of cell cycle, cell division, DNA repair and some genes linked to breast cancer. In contrast, no remarkable effect was observed in MCF-10A cell line. The designed polyphenolic mixture was demonstrated to inhibit breast cell division in multiple pathways. Our findings on cell division in MCF-7 cell line were found similarly with the study based on polyphenol-rich propolis which inhibited cell division remarkably in SK-BR-3 cells. This mixture, which is shown to have highly effective anticarcinogenic effects, can be considered as a prototype of natural prescription design for our future research.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2510.3658 Keywords Polyphenols breast cancer whole genome expression cell proliferation cell division microarray DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Chemodiversity studies on Cleome L. genera by chemical characterization of Cleome pallida Kotschy and C. fimbriata Vicary essential oils with subsequent hierarchical cluster (HCA) and principal component analysis (PCA)
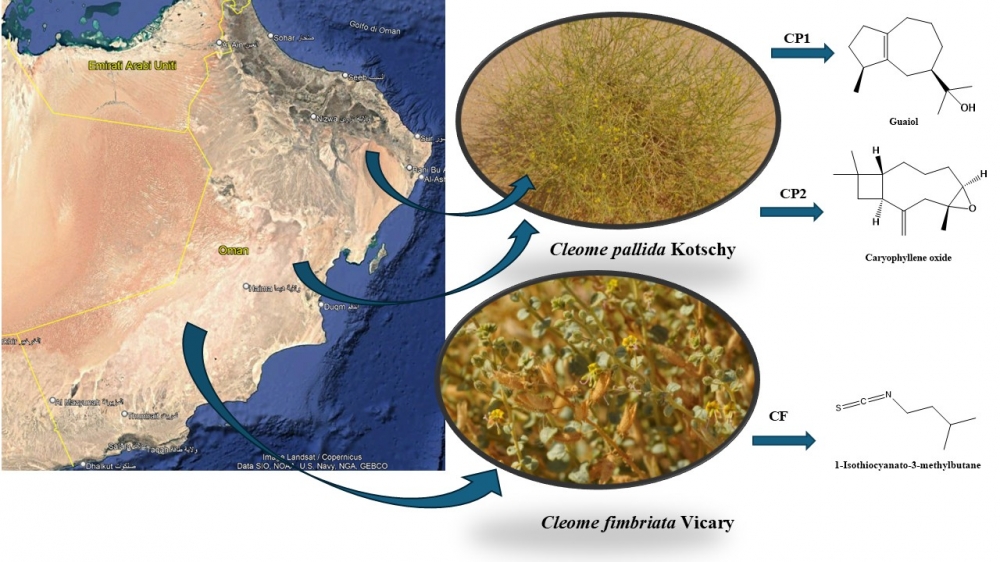
Cleome genus, belonging to the Cleomaceae family, includes about 180-199 species distributed in several countries and many of which are used extensively in ethnomedicine. In fact, many of these specimens are consumed in the form of infusions or salads to treat multiple physiological problems. In this study, the qualitative chemical composition of the essential oils obtained by hydrodistillation from Cleome ssp. was studied. Two species, two different accessions (CP1, and CP2) of C. pallida Kotschy, and one of C. fimbriata Vicary (CF), were collected in Oman and chemically investigated for the first time. The three essential oils, extracted by hydrodistillation, were analyzed by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry (GC-MS). In total, 169 compounds were identified. Sesquiterpenoids were found to be the major chemical group of CP1 and CP2 samples (56.4-58.8%); CF, instead, consisted essentially of nitrogen derivatives (30.2%), with 1-isothiocyanato-3-methylbutane (20.7%) as the most abundant class’ compound. Furthermore, a new complete review of the chemical compositions’ literature, never studied, was carried out on all other Cleome species. spontaneous in the world, studied so far. Statistical studies such as Hierarchical cluster (HCA) and principal component analysis (PCA) were employed used to highlightestablish chemo-similarities or dissimilarities, and to highpoint possible correlations between the chemical compositions of CP1, CP2, and CF, and the pharmacognosy and the reported Cleome ssp. essential oils.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2601.3788 Keywords Caryophyllene oxide ecological traits food properties 1-isothiocyanato-3-methylbutane volatile analyses DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Tenuifoliside Z1, an undescribed glycolipid from Polygala tenuifolia Willd. roots with antioxidant activity
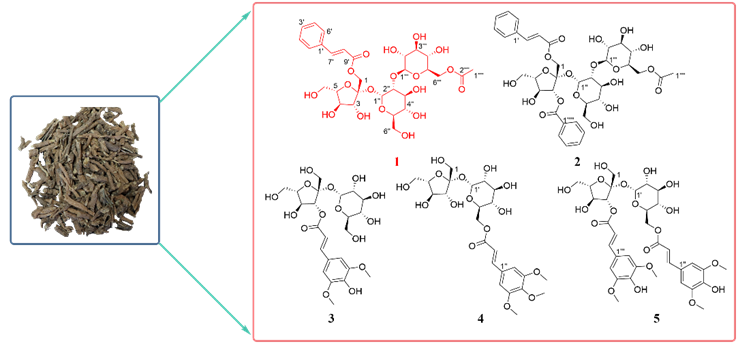
Abstract: a new glycolipid, tenuifoliside Z1 (1), together with four known glycolipid compounds (2-5) has been isolated from the root of Polygala tenuifolia Willd. Their structures were determined through spectroscopic analysis, chemical derivatization, and comparison with spectroscopic data reported in the literature. All the compounds were evaluated for antioxidant activity by in vitro assays.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2601.3791 Keywords Polygala tenuifolia Willd Polygalaceae Glycolipids Antioxidant activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Anti-inflammatory xanthones from the fruits of Hypericum patulum Thunb.
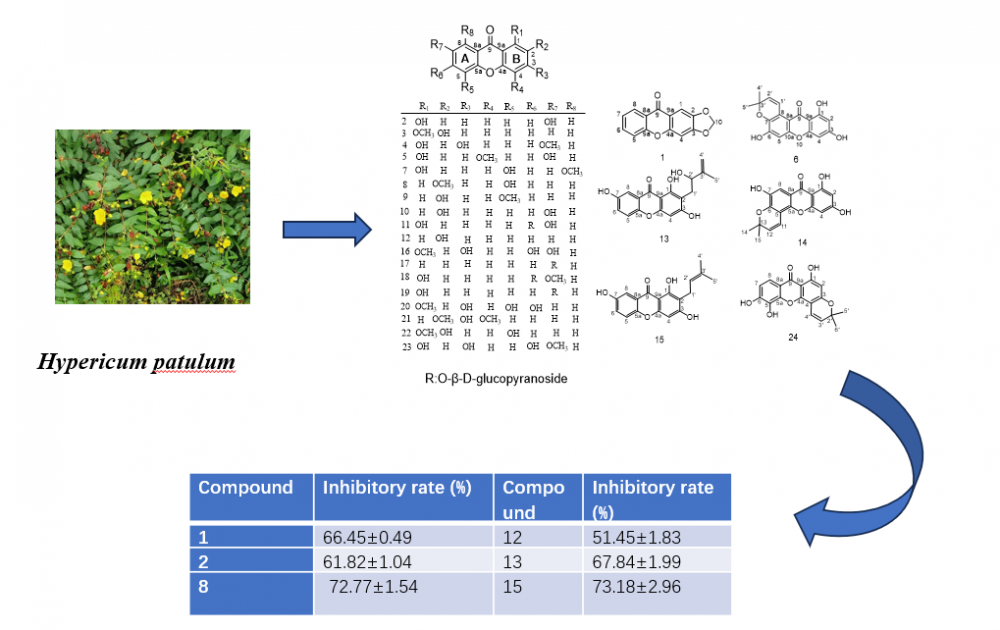
Abstract: Twenty-four known xanthones were isolated from the 80 % ethanol extract of the fresh ripe fruits of Hypericum patulum Thunb. Their structures were elucidated by extensive NMR and MS spectroscopic analysis and comparison with literature data. Compounds 4, 7, 14, and 18-19 were first reported in this genus. Compounds 1, 3, 9-11, 13, 15-17, and 20-21 were first reported from this species. Anti-inflammatory studies have shown that compounds 1-2, 8, 12-13 and 15 have a significant inhibition rate of NO release compared to dexamethasone (DEX). The anti-inflammatory activity data formed the basis for the structure-activity relationship analysis of the isolated compounds.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2512.3760 Keywords Hypericum patulum Thunb. Xanthones anti-inflammatory activity structure-activity relationship chemotaxonomy DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
