JOURNAL 3546
Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2025 Issue: 1 January-June
p.82 - 93
Viewed 1851 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
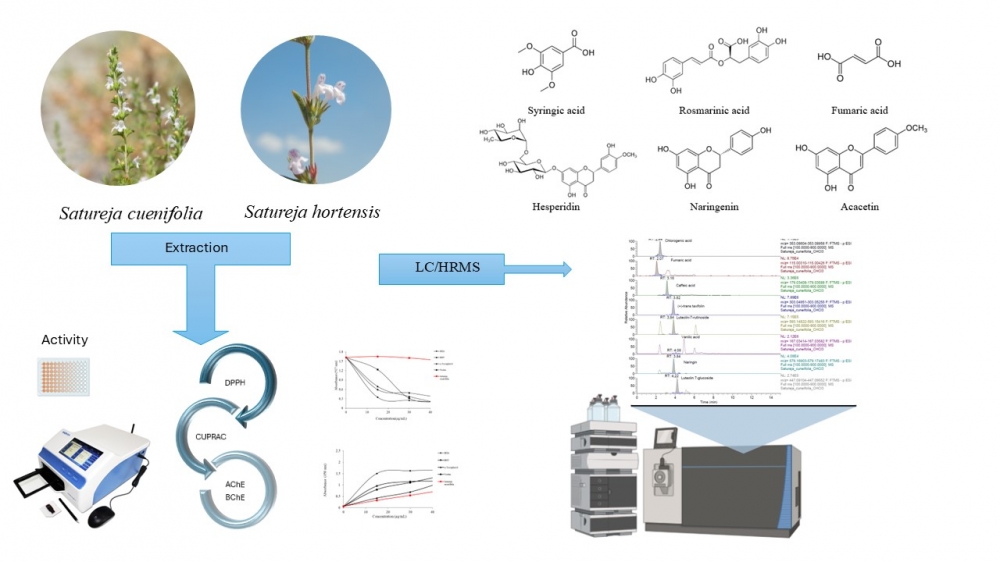
Plants are a significant source of antioxidants, including polyphenols, flavonoids, and vitamins with strong antioxidant qualities, and their use as a natural antioxidant source dates back centuries. Satureja cuneifolia Ten. and Satureja hortensis L. are two commercially important plant species consumed both as herbal tea and as spices in some regions of Türkiye. Therefore, it is very important to analyze the secondary metabolites of these plants and investigate their biological activities. In this study, the secondary metabolites of chloroform (CHCl3) and methanol (MeOH) extracts of S. cuneifolia Ten. and S. hortensis L. were analyzed by LC-HRMS. Hesperidin (702.00 mg/kg extract) and fumaric acid (472.36 mg/ g extract) were found in the CHCl3 extract of S. hortensis, whilst syringic and rosmarinic acid were the primary constituents of the MeOH extract of S. hortensis (44593.46 mg/kg extract, 37389.75 mg/kg extract, respectively) and the both extracts of S. cuneifolia (in CHCl3 926.44 and 825.42 mg/kg extract, in MeOH 55411.15 and 46045.31mg/kg extract, respectively). The extracts' antioxidant capacity was assessed using the reducing power and radical scavenging techniques, anti-Alzheimer potentials were measured by acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) enzymes inhibition experiments as in vitro. It was determined that higher activity values were present in S. cuinefolia in direct proportion to its phenolic content.
KEYWORDS- Satureja
- Satureja cuneifolia Ten
- Satureja hortensis L.
- LC-HRMS
- secondary metabolite.