JOURNAL 3555
Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2025 Issue: 1 January-June
p.103 - 113
Viewed 1863 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
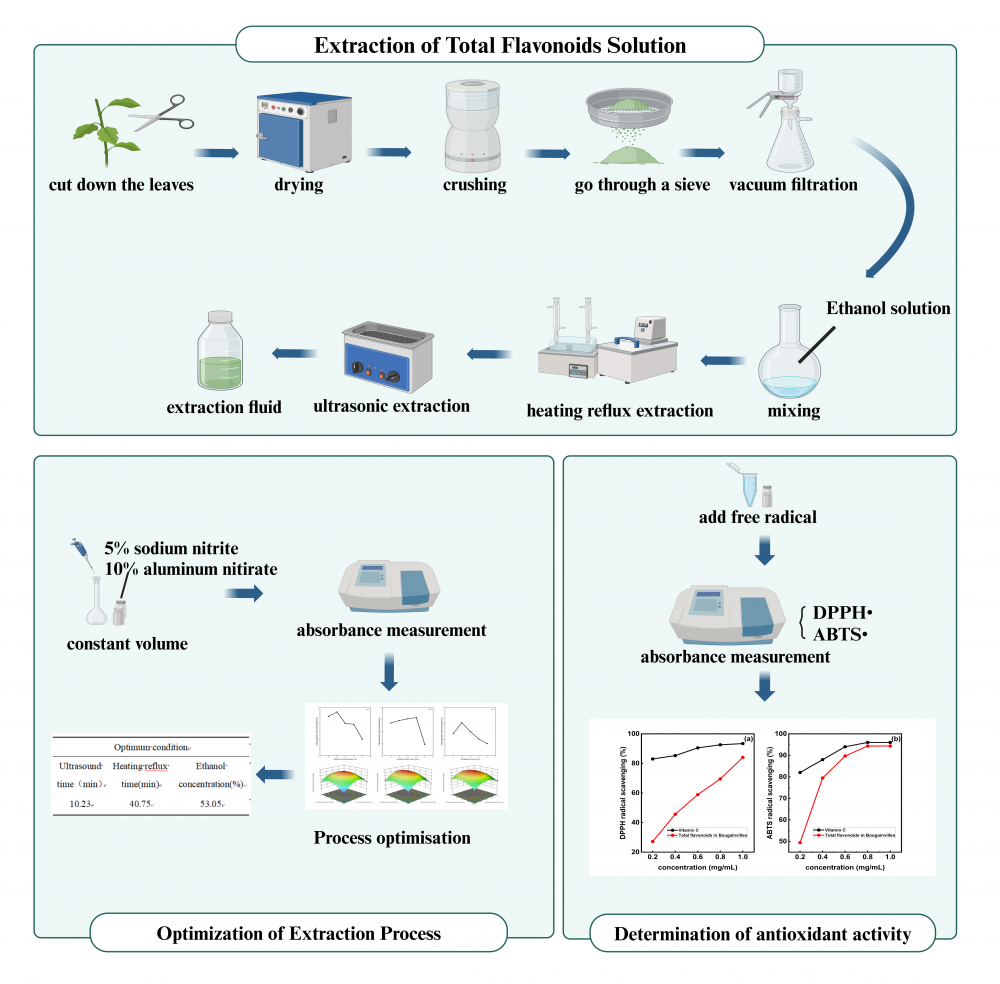
This study systematically investigated the optimization of total flavonoid extraction from the leaves of Bougainvillea glabra Choisy (B.glabra) and evaluated its antioxidant potential. The impact of three critical parameters (ultrasound time, heating reflux time, and ethanol concentration) on extraction efficiency was investigated using ultrasonication-assisted heat reflux extraction. A three-factor, three-level Box-Behnken design (BBD) was implemented to optimize the extraction procedure, using total flavonoid yield (TFY) as the response variable. The extracted flavonoids' antioxidant potential was measured quantitatively in vitro. The ideal conditions were 53% ethanol concentration, 10 minutes of ultrasonication, and 41 minutes of reflux. This procedure produced a TFY of (6.21 ± 0.26)%. The extracts exhibited significant free radical scavenging action against 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) radical and 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radical. When the concentration exceeded 1.0 mg/ mL, the scavenging rate of DPPH free radicals surpassed 84.1%. When the concentration was more than 0.6 mg/ mL, the ability of total flavonoids to scavenge ABTS free radicals was over 93.8%, which was very similar to how well vitamin C worked. This optimized protocol proves effective for flavonoid extraction, with the obtained products exhibiting significant antioxidant properties in standardized assays.
KEYWORDS- Bougainvillea
- ultrasound-assisted extraction
- total flavonoids
- Box-Behnken response surface methodology
- antioxidant activity