JOURNAL 1417
Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Reports
Year: 2019 Issue: 1-2 (January-December)
p.1 - 14
Viewed 3903 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
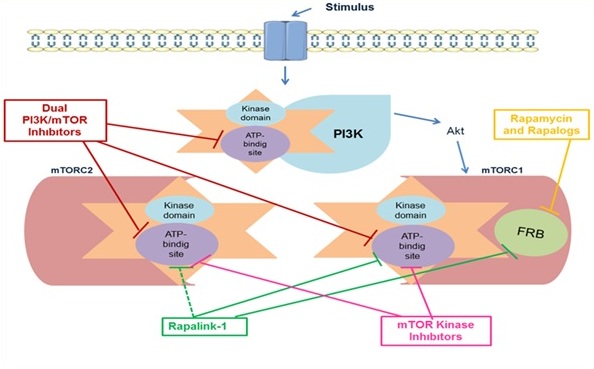
mTOR, a member of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase family, controls major physiological cellular processes such as growth and metabolism in response to nutrients, growth factors, and cellular energy levels. Furthermore, deregulation of the mTOR activity has been associated with various pathological conditions such as cancer, diabetes, obesity, neurological diseases, and genetic disorders. Therefore, research on the mTOR signalling pathway and the development of effective molecules on this pathway has been continuing intensively in recent years. In the past decade, numerous mTOR inhibitors have been developed and many are currently in clinical trials. These molecules are classified as Rapamycin and its analogs (all are termed rapalogs), ATP-competitive dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors, mTOR kinase inhibitors, and Rapa Links. In this review, we aimed to summarize current findings on mTOR signalling network and molecules acting on this signalling pathway.
KEYWORDS- mTOR
- mTOR inhibitors
- rapalogs
- dual inhibitors
- kinase inhibitors
- rapaLinks