JOURNAL 3703
Journal of Chemical Metrology
Available Online: December 07,2025
p.1 - 16
http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.125.2510.3703 (DOI number will be activated after the manuscript has been available in an issue.)
Viewed 9 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
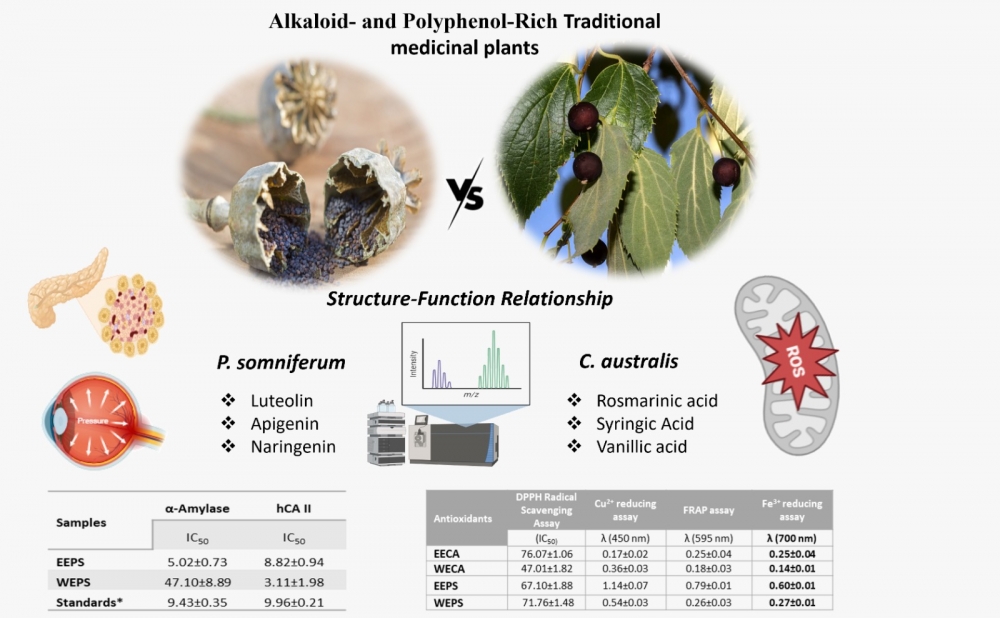
ABSTRACT
This study involves a comparative evaluation of Papaver somniferum L. (Papaveraceae) and Celtis australis L. (Cannabaceae), two phytochemically different medicinal plants from Türkiye, by focusing on their phenolic content, antioxidant capacity, and enzyme inhibition properties. Ethanolic and aqueous extracts of both plants were analyzed by LC–MS/MS, and the results revealed different secondary metabolites. P. somniferum was determined to be rich in terms of flavonoids, including luteolin, apigenin, and naringenin. Meanwhile, C. australis was found to be rich in terms of phenolic acids, including rosmarinic, syringic, vanillic, and chlorogenic acids. Antioxidant evaluation through ABTS radical scavenging, CUPRAC, FRAP, and Fe³⁺-reducing assays showed that the aqueous extract of C. australis (WECA) exhibited significant radical scavenging capacity; on the other hand, the ethanolic extract of P. somniferum (EEPS) possessed stronger reducing power, which was evaluated as consistent with their respective phenolic compositions determined by LC-MS/MS analysis. Enzyme inhibition assays of both extracts demonstrated potent α-amylase inhibition by EEPS with an IC50: 5.02±0.73 µg/mL, suggesting potential antidiabetic effects, and remarkable human carbonic anhydrase II (hCA II) inhibition by P. somniferum water extract with IC50: 3.11±1.98 µg/mL, outperforming the standard inhibitor. Both plants also showed moderate anticholinergic effect, indicating a possible neuroprotective property. In conclusion, while the flavonoid-rich P. somniferum showed excellent reducing ability and potent inhibition of key metabolic enzymes, including α-amylase, AChE, and hCA II, the phenolic acid–dominant C. australis exhibited a stronger radical scavenging efficiency, reflecting distinct yet complementary antioxidant and therapeutic potentials that may be harnessed for functional or pharmacological applications.
KEYWORDS- Papaver somniferum
- Celtis australis
- LC-MS/MS
- antioxidant activity
- enzyme inhibition