JOURNAL 1555
Organic Communications
Year: 2020 Issue: 1 January-March
p.19 - 27
Viewed 3730 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
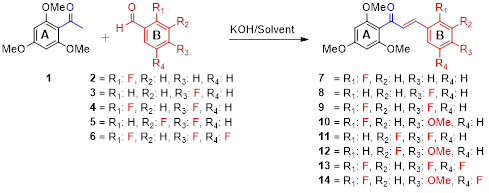
In this study, 2′,4′,6′-Trimethoxyacetophenone was reacted with various fluorine-substituted benzaldehydes in the presence of an aqueous solution of 50%-potassium hydroxide, and new chalcone derivatives in the structure of 1,3-diaryl-2-propenone comprising both fluorine and methoxy groups in the aromatic B ring were obtained in high yields under mild conditions. In base-catalyzed Claisen-Schmidt condensations, MeOH is usually used as solvent. In the condensation reactions performed with mono-fluorine-substituted benzaldehydes in MeOH, the corresponding fluorine-substituted chalcone derivatives in the B ring were synthesized in high yield. On the other hand, when di- and tri-fluorine-substituted benzaldehydes were used, it was determined that a nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr) occurred in the reaction condition and the condensation yield decreased. Consequently, fluorine-methoxy substituted chalcone derivatives were isolated by substitution of fluorine and methoxy group in para position in the aromatic B ring. On the other hand, it was found that when THF was used as the reaction solvent, chalcone derivatives carrying only fluorine atoms could be obtained with excellent chemical selectivity without any competitive aromatic nucleophilic substitution (SNAr) in the condition. Particularly in the synthesis studies of such fluorine-substituted chalcones, it was determined that the Claisen–Schmidt condensation ratio is dependent on the effect of the solvent in addition to steric and electronic factors.
KEYWORDS- Fluorine
- methoxy
- chalcone
- synthesis