JOURNAL 1796
Organic Communications
Year: 2020 Issue: 3 July-September
p.127 - 137
Viewed 3478 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
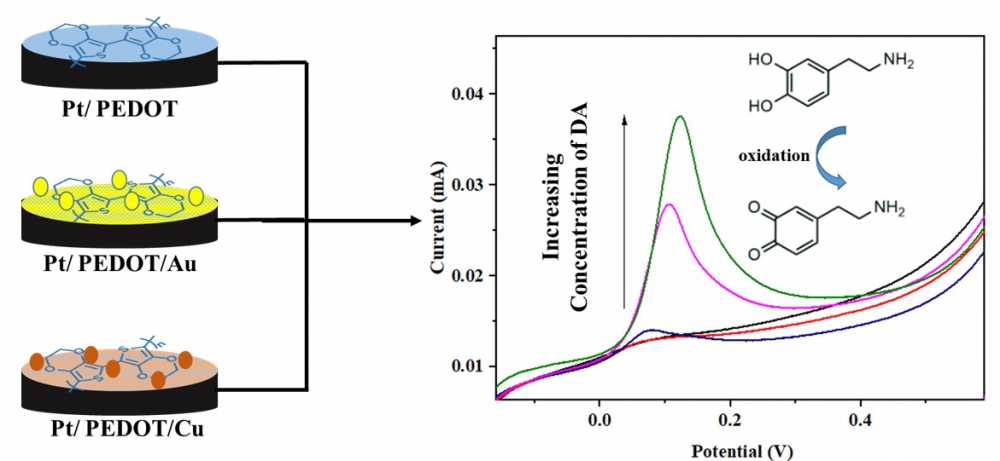
ABSTRACT
Hormones are important and necessary for the continuity of many vital functions in human body. Dopamine (DA) is a neurotransmitter affecting pain and pleasure perceptions, emotions, and movements. In the case of DA deficiency, severe discomforts such as Schizophrenia and Parkinsonism may happen. Thus, DA detection is an important subject. Electrochemical methods have been used in this work by developing a sensor for rapid and easy detection of DA. 3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) monomer was polymerized on a platinum electrode using cyclic voltammetry method, and the film properties of the resultant polymer were investigated. Additionally, gold and copper coated PEDOT films, Pt/PEDOT/Au and Pt/PEDOT/Cu, respectively, were prepared to improve the sensitivity and stability of the films, compared to Pt/PEDOT electrode. The calibration curves were found to be linear in the concentration range of 50-1000 μM for DA in the presence of ascorbic acid (AA). The detection limits were determined as 18.46 μM, 13.33 μM and 6.80 μM for Pt/PEDOT, Pt/PEDOT/Cu and Pt/PEDOT/Au electrodes, respectively. Moreover, the electrodes demonstrated an electrochemical catalytic effect toward DA.
KEYWORDS
- 3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT)
- PEDOT
- Au and Cu nanoparticles,
- electrochemical polymerization,
- biosensor
- dopamine