JOURNAL 3039
Organic Communications
Year: 2024 Issue: 1 January-March
p.8 - 22
Viewed 2029 times.
-
Babai Mahdi

-
Mohamad Nurul Azmi

-
Lacksany Phongphane

-
Muhammad Solehin Abd Ghani

-
Mohamad Hafizi Abu Bakar

-
Mohammad Tasyriq Che Omar

-
Andrey A. Mikhaylov

-
Unang Supratman

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
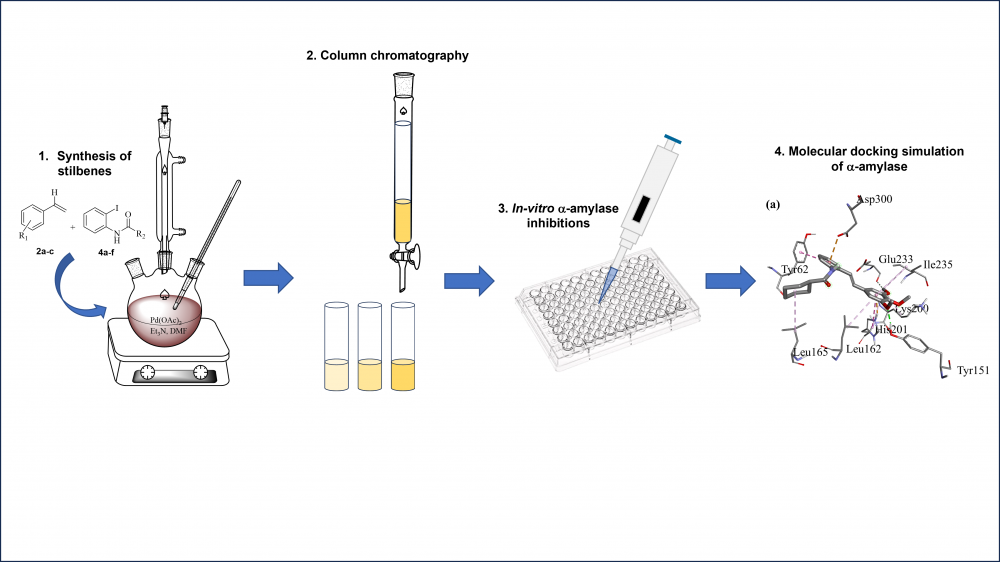
Due to the recent emergence of drug-resistance of antidiabetic drugs and increase in the number of diabetes cases around the world, the search for and discovery of more effective α-amylase inhibitors is of great interest. In the present study, a new series of eighteen ortho-carboxamidostilbene derivatives were synthesized via Heck coupling reaction. The structures of the synthesized compounds were identified by various spectroscopic techniques, including HRMS, FTIR and 1D-NMR. In addition, the compounds were evaluated in vitro for their potential α-amylase inhibitory potency using acarbose as the reference drug. Compounds 5e, 5f and 6e showed remarkably moderate to good inhibitory activity with IC50 values ranging from 13.3 − 28.2 µM. These compounds showed the potent IC50 values compared to the reference drug acarbose (IC50 = 30.2 ± 0.1). The in-silico molecular docking studies revealed that the binding interactions of the most active ortho-carboxamidostilbene derivatives (5e and 6e) with binding energies of -8.7 ± 0.0 and -8.6 ± 0.2 kcal/mol. Based on the structure-activity relationship (SAR) analysis, it was established that variations in the inhibitory activities of α-amylase enzymes were attributed to distinct types of substituents at the amide group of aryl ring A, and the number and position of methoxy groups attached to aryl ring B. These findings highlight α-amylase inhibitory properties of ortho-carboxamidostilbene-containing cyclohexyl and benzyl moieties, serving as potential lead compounds in antidiabetic drug development for the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus.
KEYWORDS- Ortho-carboxamidostilbene
- Heck coupling
- diabetes
- α-amylase
- molecular docking