JOURNAL 3595
Organic Communications
Available Online: August 31,2025
p.1 - 11
http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.195.2507.3595 (DOI number will be activated after the manuscript has been available in an issue.)
Viewed 201 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
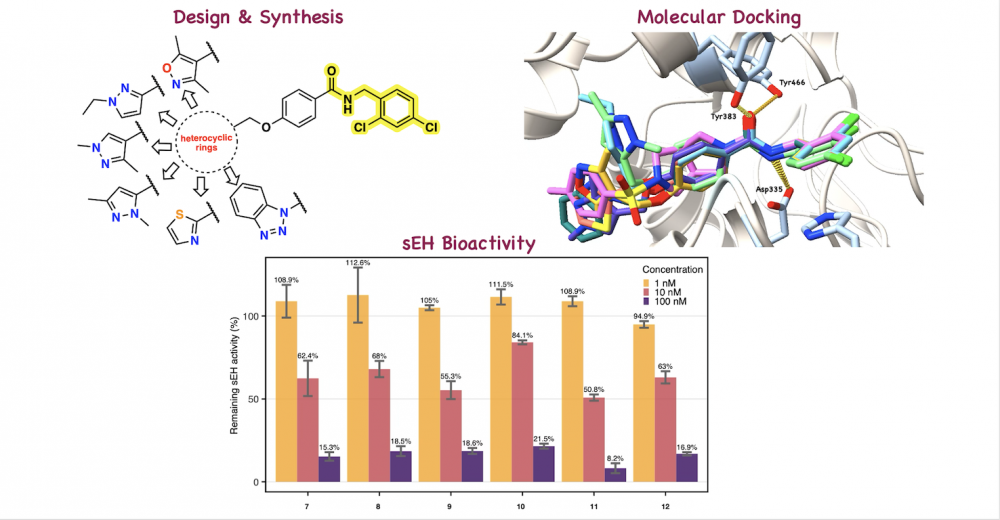
ABSTRACT
A novel series of amide-based soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitors was rationally designed by incorporating 2,4-dichlorobenzyl and terminal heterocyclic moieties into a central amide scaffold. The target compounds were synthesized and structurally confirmed as new chemical entities using HRMS, 1H NMR, and 13C NMR spectroscopy. Molecular docking studies of the synthesized inhibitors with sEH revealed key hydrogen bonding interactions with Asp335, Tyr383, and Tyr466, along with π–π stacking interactions with His524 and Trp525, indicating their effective binding to the sEH active site. In vitro biological evaluation showed that all synthesized derivatives exhibit potent sEH inhibitory activity at both 10 and 100 nM, with compound 11 emerging as the most promising lead for further development of potent anti-inflammatory agents.
KEYWORDS- Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids
- soluble epoxide hydrolase
- heterocyclic compounds
- amide-based inhibitors