JOURNAL 2487
Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Year: 2022 Issue: 2 July-December
p.84 - 93
Viewed 2366 times.
-
Mathieu Sawalda

-
Tamfu Alfred Ngenge

-
Fadimatou

-
Cadet François Essongue

-
Emmanuel Talla

-
Henoumont Céline

-
Laurent Sophie

-
Farzana Shaheen

-
Joseph Tanyi Mbafor

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
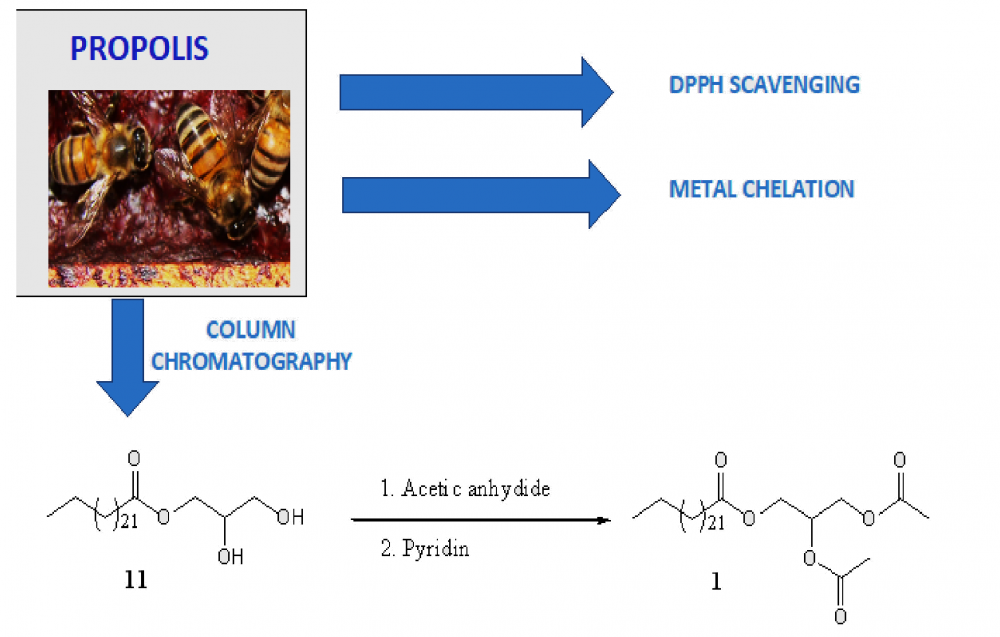
Five extracts were prepared from different propolis samples and denoted PR1-PR5. They were subjected to two complementary antioxidant assays, DPPH radical scavenging and metal chelation. The propolis extracts PR4 and PR5 showed good radical scavenging power with IC50 20.45 ± 1.65 μg/mL and 17.23 ± 1.40 μg/mL respectively as well as appreciable chelating power of IC50 7.52± 0.61 µg/mL and 3.47± 0.61 µg/mL for PR4 and PR5 respectively. The PR1 extract showed a moderate radical scavenging activity with an IC50 = 230.08 ± 18.60 μg/mL and exhibited a high chelating power with an IC50 of 17.40 ± 1.41 μg /mL. This potent antioxidant effects of the propolis indicates its possible application in food science. Some compounds were isolated and characterized by 1D-, 2D-NMR studies as 7-O-ß–glucopyranosylapigenine, fridelin, lupeol, β-sitosterol, 3'-hydroxypentyltetratretracontanoate, 3'-hydroxybutyltetracontanoate, propylhexatetracontanoate, methyl-tetratretraconta-noate, 1′-O-eicosanylglycerol, and 2',3'-dihydroxypropyltetraeicosanoate which was further acetylated through hemi-synthesis to yield 2',3'-diacetylpropyltetraeicosanoate.
KEYWORDS- Propolis
- radical scavenging
- metal chelation
- acetylation
- 2,3-diacetylpropyltetraeicosanoate