JOURNAL 3029
Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Year: 2024 Issue: 3 Special Issue: Abstracts 3rd. TCS, International Food Chemistry Congress February 29-March 03,2024 Antalya Türkiye
p.52 - 52
Viewed 1493 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
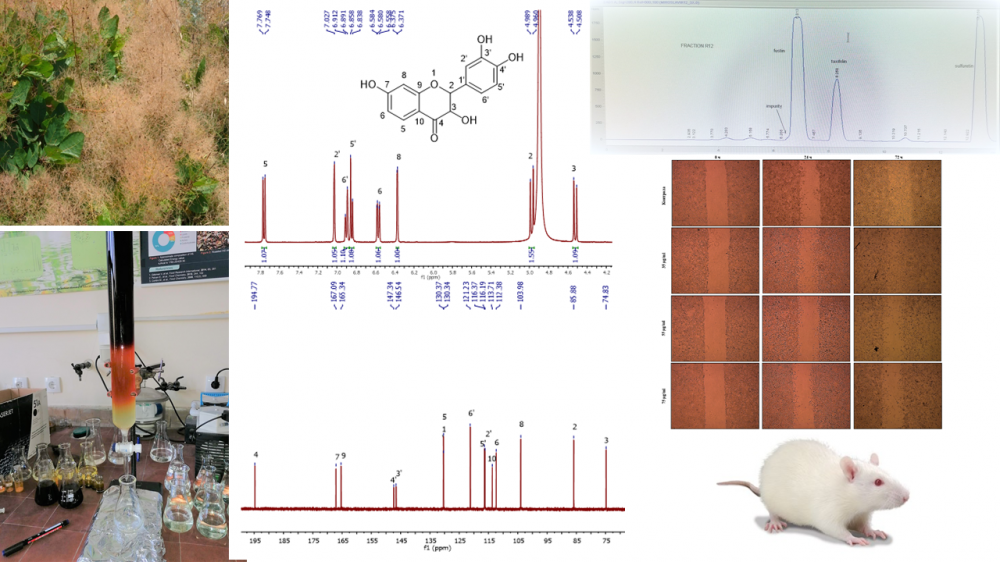
The research on medicinal plants and their biologically active components, and the identification of new molecular targets is relevant to the development of new remedies and functional foods. Eurasian Smoketree (Cotinus coggygria Scop., Anacardiaceae) is a popular medicinal plant with a significant therapeutic potential, widely distributed from Southern Europe to Central China. It has a high content of polyphenols, including the flavanonol fustin, which is poorly studied for biological activity in preclinical experiments. The aim of the present study was to isolate and purify fustin from the heartwood of Eurasian Smoketree (C. coggygria) by appropriate extraction procedure. C. coggygria heartwood was collected at the Protected Area “Deliblato Sand”, Vojvodina province, Serbia, in May 2022. Plant material was identified by Prof. Milan Veljic, Faculty of Biology, University of Belgrade, and compared to Herbarium specimen BEOU 17422 of the Institute of Botany and Botanical Garden in Belgrade, Serbia. The heartwood was air-dried and milled to a fine powder. Quantity of 1 kg of wood powder was extracted three times with 10 L of methylene chloride/methanol 1:1 for 24 h at room temperature and extracts were combined. After evaporation, 76 g of crude extract was fractionated by column chromatography (CC) on Merck silica gel column (750 × 45 mm) with particle size 0.063-0.200 mm, using methylene chloride-methanol gradient solvent system as a mobile phase with increasing methanol content. CC was screened by analytical thin layer chromatography (TLC) on aluminium plates precoated with Merck silica gel 60 F254 (0.25 mm thickness), and the fractions with similar retardation factor (Rf) values were combined. Fustin-rich fractions, detected by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy were eluted with methylene chloride/methanol at approximately 90/10 to 80/20. Those fractions were used for further purification and isolation of fustin by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) following the method described by Novakovic et al. (2019) [1]. Pure fustin was isolated from these fractions by reversed-phase (RP) semi-preparative HPLC on an Agilent Technologies 1100 Series HPLC-DAD with Zorbax Eclipse XDB C18 column (150 × 9.4 mm, i.d. 5 μm) at 254 nm for detection, and water/acetonitrile system using the following program: 0-20 min, 20-37% CH3CN; 20-21 min, 37-50% CH3CN; 21-27 min, 50% CH3CN; and 27-30 min, 50-100% CH3CN. Fustin was purified up to 98% on RP-HPLC using the following program: 0-20 min, 25-40% CH3CN (Rt= 5.1 min). NMR-spectroscopy was used for the structure elucidation. Fustin purity was proved by HPLC and NMR. The NMR spectra were obtained on a Bruker Avance III 500 (500 MHz for 1H; 125 MHz for 13C), in CD3OD as solvent. Chemical shifts (δ) were expressed in ppm and coupling constants (J) in hertz (Hz). As a result, 1.01 g fustin (≥98% purity) was isolated and further used in tests for biological and pharmacological activity on cell cultures and Wistar rats.
KEYWORDS- fustin
- silica gel column chromatography
- semi-preparative HPLC
- NMR spectroscopy