JOURNAL 3115
Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Year: 2024 Issue: 3 Special Issue: Abstracts 3rd. TCS, International Food Chemistry Congress February 29-March 03,2024 Antalya Türkiye
p.76 - 76
Viewed 1622 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
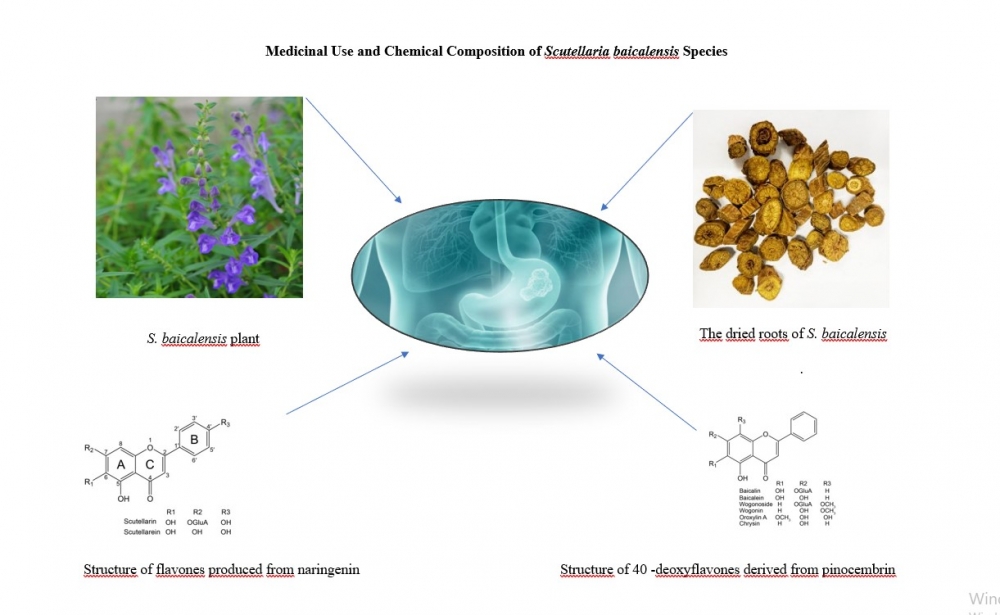
This work deals with the medicinal use and chemical composition of the Scutellaria genus. The Scutellaria genus, which belongs to the Lamiaceae family, is represented by approximately 360 species. In Turkey, the Scutellaria genus includes 15 species belonging to 4 sections and a total of 21 subspecies of these species [1,2]. Scutellaria baicalensis, known also as Huang-Qin is a traditional Chinese plant used in medicine for at least 2000 years. The plant is widely distributed in Japan, Korea, Mongolia and Russia, and is listed in Chinese Pharmacopoeia, European Pharmacopoeia and British Pharmacopoeia [3]. Medicinal plants in the Scutellaria genus are used in the treatment of various diseases such as gastrointestinal diseases (dysentery, hemorrhoids, stomach pain, constipation), liver and bile diseases (jaundice, hepatitis), neurological diseases (including epilepsy, spasm, insomnia, hysteria). It is also stated in the literature that it is also used in respiratory diseases (colds, respiratory tract infections), infectious diseases (carbuncles, furunculosis) and traumatic injuries It has been stated that some species of Scutellaria have a long history as traditional and herbal medicine to treat many diseases such as cancer, liver and stomach disorders, respiratory, neurological, cardiovascular diseases and infection [4]. It has been stated that S. baicalensis has a very good antioxidant activity thanks to its rich flavonoid content [5]. Some of the diterpenes in the Scutellaria genus are scutesiprine and barbatin A-E, and their compounds have been stated to have anticancer effects [6,7]. The main bioactive compounds of S. baicalensis are flavonoids. The total flavonoid content in plant roots varies between 15-20 %. Flavonoids are 12-16 % baikalin, baikalayin, norvoginin, oroxylin A, β-sitosterol and 3-4 % vogonocyte [8].
KEYWORDS- Scutellaria baicalensis
- medicinal uses