JOURNAL 3007
Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Year: 2024 Issue: 3 Special Issue: Abstracts 3rd. TCS, International Food Chemistry Congress February 29-March 03,2024 Antalya Türkiye
p.13 - 13
Viewed 1655 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
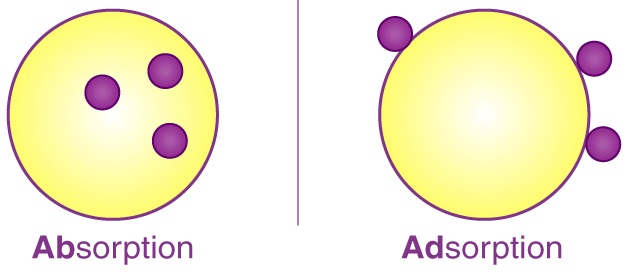
This study explores the viability of herbal tea as an eco-friendly solution for water remediation. Herbal teas, including hibiscus, mint, and chamomile, are rich in bioactive compounds such as antioxidants and polyphenols, known for their ability to absorb various contaminants present in water. Therefore, this investigation focused on chamomile tea's ability to remove lead from aqueous solutions. Systematic variations in adsorbent quantity, solution concentration, mixing conditions, and pH levels [1] were conducted to identify optimal experimental parameters. Quantitative assessment of metal concentration, specifically lead (Pb) pre-and post-treatment, was performed using ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry). The morphological characteristics of the biosorbents were explained through SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy). The outcomes of the study revealed exceptional efficacy, underscoring the potential of these agricultural waste-derived materials for practical use in daily water treatment. The biosorbents demonstrated significant advantages over conventional methods, including cost-effectiveness, high selectivity, and biodegradability, positioning them as promising candidates for sustainable water purification applications.
KEYWORDS- Chamomile residues
- heavy metal
- ICP-OES
- SEM