JOURNAL 1262
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2020 Issue: 1 January-February
p.65 - 76
Viewed 4191 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
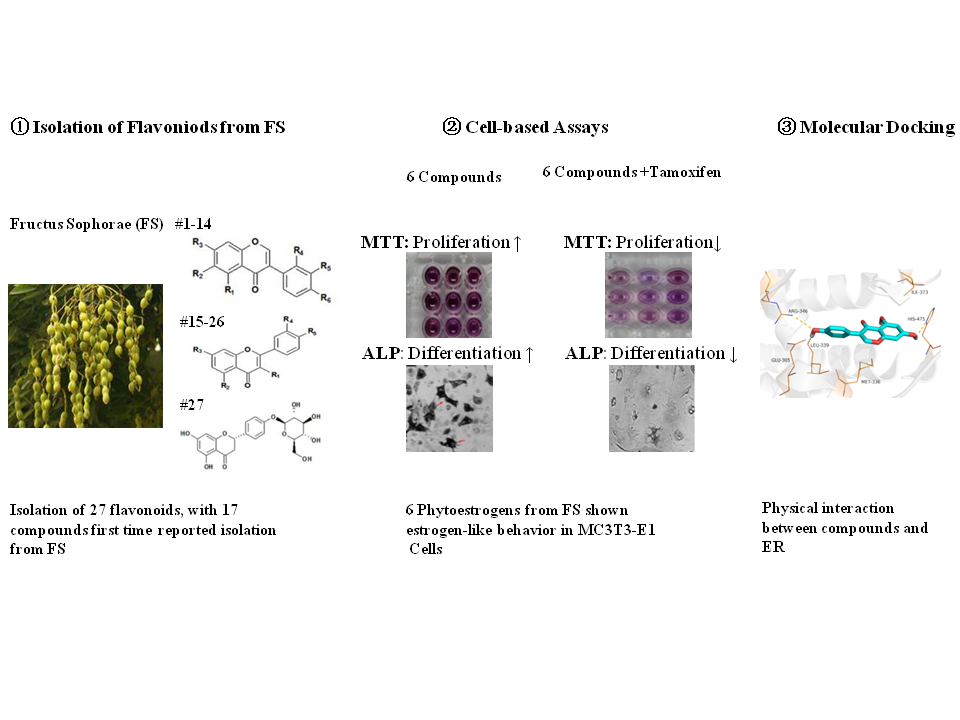
Fructus Sophorae (FS), the dry mature fruit of Sophora japonica Leguminosae, is a valuable traditional Chinese medicine resource with flavonoids as the major active ingredients. To identify the plant-derived estrogen-like flavonoids serving as potential osteoporosis chemopreventive agents, we isolated and identified 27 flavonoids compounds, including 17 compounds obtained for the first time from FS. To screen out the flavonoids with estrogen-like biological behavior from the 11 high yield compounds, we set up an in vitro screening system in rat osteoblast MC3T3-E1 cells including MTT assay, alkaline phosphatase staining and Alizarin red S staining assay to examine the effects on cell proliferation, differentiation and mineralization of osteoblast cells respectively. Six flavonoids, including genistein, sophoricoside, sophorabioside, sophoraflavonoloside, nicotiflorin and rutin, significantly increased the cellular activity of MC3T3-E1 cells. Furthermore, blocking the estrogen receptor signaling by tamoxifen compromised the effects above significantly, suggesting the 6 compounds behave as estrogen-like reagents. Moreover, the interaction between the six flavonoids from FS and estrogen receptor was clarified by molecular docking method from Glide XP. Collectively, being used as food and medicine in China, FS is rich in flavonoids with estrogen-like effects, may be used as healthy supplementary in treating postmenopausal women osteoporosis.
KEYWORDS- Fructus Sophorae
- Flavonoid
- Phytoestrogens
- Estrogen Receptor
- Osteoporosis