JOURNAL 1224
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2020 Issue: 1 January-February
p.23 - 30
Viewed 3783 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
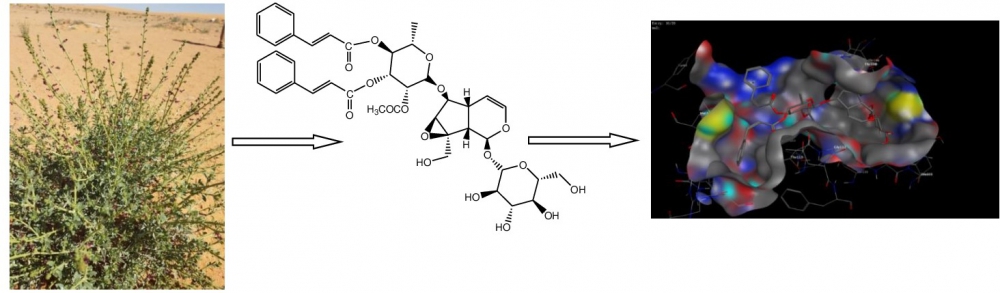
ABSTRACT
Phytochemical study of the ethanolic extract of Scrophularia syriaca Benth. was attained by chromatographic and spectroscopic procedures, which resulted in isolation of eight compounds; 6-O-α-L- rhamnopyranosylcatalpol (1), scropolioside B (2), gmelinoside-L (3), 8-acetyl harpagide (4), scropolioside D (5), scropolioside D2 (6), quercetin (7) and kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside (8). The antiprotozoal activity was evaluated against Trypanosoma brucei brucei (s427-WT), Trypanosoma brucei brucei (TbAT1-B48), Leishmania major and Leishmania mexicana. Compounds 2, 5, 7 and 8 exhibited mild to moderate activities against kinetoplastid parasites compared to pentamidine positive control, the mechanism of antiprotozoal activity was predicted by the molecular docking studies on the target enzyme Trypanosoma brucei glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (TbGAPDH).
KEYWORDS- docking
- iridoids
- Leishmania
- Trypanosoma
- Scrophularia syriaca
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
Scrophularia Syriaca photo

a photo of Scrophularia Syriaca plant growing in northern Saudi Arabia in the flowering stage