JOURNAL 1692
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2021 Issue: 2 March-April
p.91 - 102
Viewed 3506 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
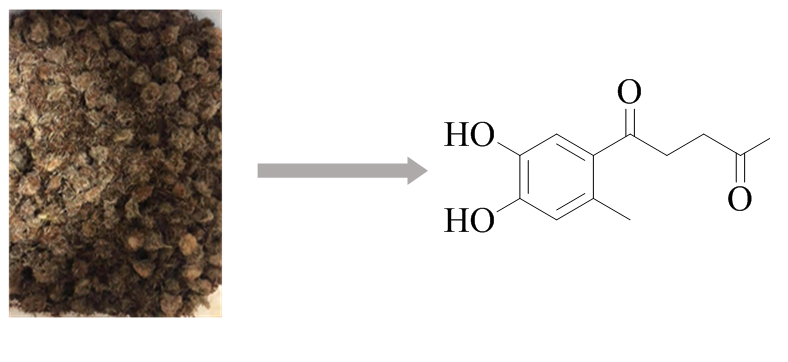
ABSTRACT
One new phenolic derivative, 1-(4',5'-dihydroxy-2'-methylphenyl)-pentane-1,4-dione (1), along with eighteen known compounds including eight sesquiterpenoids (2–9), one triterpenoid (10), one bisdpoxylignan (11), one coumarin (12), and seven flavonoids (13–19) were isolated from the dried inflorescence of Tibetan herbal medicine Pulicaria insignis. The structure of 1 was established by spectroscopic methods, including HRESIMS, IR, 1D, and 2D NMR. All isolates were assessed for the cytotoxic activities against MGC-803, T24, HepG2, and HeLa cell lines using the MTT assay. The results showed that compound 1 displayed moderate cytotoxicity against Hela and HepG2, and compounds 3, 4, 5, 6, and 13 exhibited potential cytotoxic activities against the four cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 3.05 to 14.37 μM. Notably, compound 5 exhibited significant anti-proliferative activities against HepG2 cell lines with the IC50 values of 3.05 ± 0.36 μM. Further bioactivity investigation showed that compound 5 could block HepG2 cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, thereby inhibiting the growth of HepG2 cells and inducing apoptosis in HepG2 cells.
KEYWORDS- Pulicaria insignis
- chemical constituent
- phenolic derivative
- cytotoxic activity
- sesquiterpenoid