JOURNAL 1854
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2021 Issue: 4 July-August
p.324 - 329
Viewed 3060 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
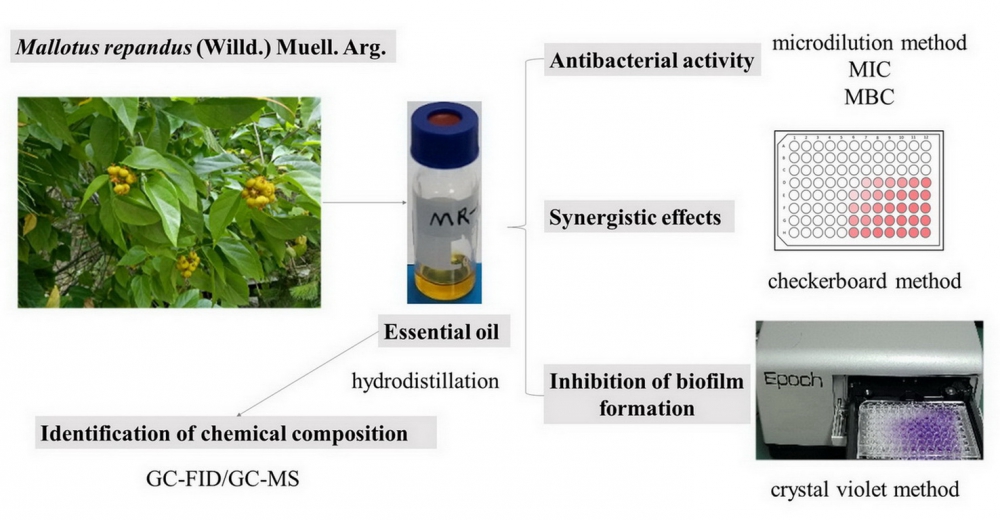
ABSTRACT
The essential oil (EO) of aerial parts of Mallotus repandus (Willd.) Muell. Arg. was extracted by hydrodistillation and characterized by GC/FID and GC/MS. Fifty-one compounds comprising 97.1% of the EO were identified, of which α-humulene (18.7%), β-selinene (12.8%), aciphyllene (10.7%), (E)-caryophyllene (8.4%), α-copaene (5.5%), humulene epoxide II (4.9%) and caryophyllene oxide (4.3%) were the major compounds. The EO was evaluated for antibacterial properties using broth microdilution method and crystal-violet static biofilm formation assay. The M. repandus EO possessed a bactericidal effect against tested gram-positive bacteria strains (MIC = MBC: 0.05-0.10 mg/mL). Further, the EO showed the ability to inhibit the biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus. In addition, the potential synergistic effect was assessed by checkerboard method. Combination of the M. repandus EO with Streptomycin showed synergistic effects against the tested bacterial strains. This study demonstrates that M. repandus EO could be further explored as good alternative for potential pharmaceuticals.
KEYWORDS- Mallotus repandus (Willd.) Muell. Arg.
- essential oil
- antibacterial activity
- antibiofilm activity
- synergistic effects