JOURNAL 1929
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2021 Issue: 5 September-October
p.396 - 407
Viewed 2897 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
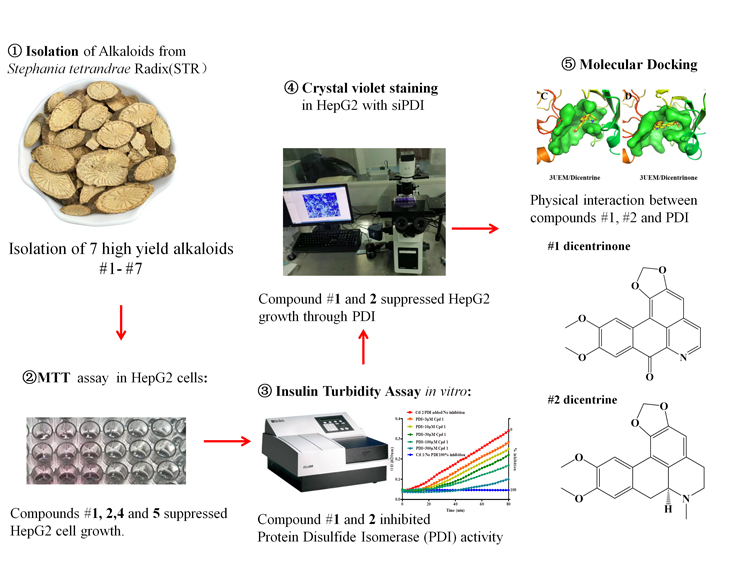
ABSTRACT
Inhibition of protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) has been attempted as a promising anti-cancer strategy. However, there is still no currently available PDI inhibitors approved for clinical use. Here, we isolated seven high yield alkaloids from Stephaniae tetrandrae Radix (STR), a medical herb frequently prescribed in anti-tumor condition, and identified two potent natural PDI inhibitors, dicentrine and dicentrinone. Among the seven alkaloids isolated, dicentrinone (1), dicentrine (2), tetrandrine (4), and fangchinoline (5) could significantly reduce cell viability in a dosage dependent manner detected by MTT assay in human hepatoma cells. To examine whether the candidate compounds are potent PDI inhibitors, we performed insulin turbidity assay and found dicentrine and dicentrinone, but not tetrandrine and fangchinoline, could effectively inhibit PDI activity, with IC50 of 56.70 μM and 43.95 μM respectively. Meanwhile, dicentrine and dicentrinone failed to further reduce the cell number index when co-treated with siRNA of PDI, suggesting the compounds behave as PDI inhibitors. Furthermore, dicentrinone and dicentrine have been successfully docked to the active pocket of PDI (PDB #3UEM) by molecular docking, suggesting the existence of physical interaction between compounds and PDI. Our results suggested that dicentrine and dicentrinone may be developed into safe PDI inhibitors.
KEYWORDS- Stephania tetrandrae Radix
- Dicentrine
- Dicentrinone
- HepG2
- PDI