JOURNAL 2240
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Issue: 5 September-October
p.477 - 482
Viewed 3342 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
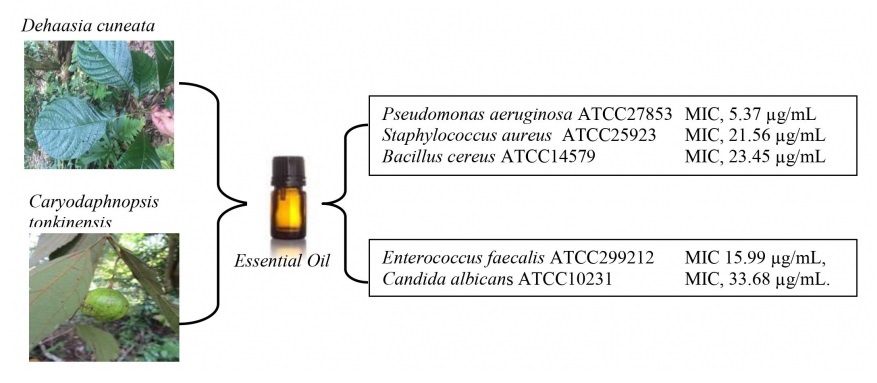
The herbs, Dehaasia cuneata (Blume) Blume and Caryodaphnopsis tonkinensis (Lecomte) Airy-Shaw (Lauraceae) were used ethnomedically for the treatment of malaria, inflammation and amelioration of microbial infections. We report herein the chemical constituents and antimicrobial activity of the leaf essential oils of D. cuneata and C. tonkinensis from Vietnam. The technique of gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC/MS) was used to analyze the oil samples while the microdilution assay was employed to determine the antimicrobial efficacy. The main constituents of D. cuneata were α-pinene (49.0%), camphene (19.5%), β-pinene (15.6%) and limonene (7.5%), while α-pinene (26.8%), β-pinene (23.0%) and bicyclogermacrene (8.5%). The leaf oil of D. cuneata displayed potent antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC27853 with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value of 5.37 µg/mL; and Gram-positive microorganisms of Staphylococcus aureus ATCC25923 (MIC, 21.56 µg/mL and Bacillus cereus ATCC14579 (MIC, 23.45 µg/mL). The leaf oil of C. tonkinensis exhibited good antibacterial activity towards Enterococcus faecalis ATCC299212 with MIC value of 15.99 µg/mL, and anti-candidal action against Candida albicans ATCC10231 with MIC value of 33.68 µg/mL. the chemical constituents and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils were being reported for the first time.
KEYWORDS- Antimicrobial activity
- essential oil composition
- terpenes