JOURNAL 2314
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Issue: 6 November-December
p.639 - 644
Viewed 3541 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
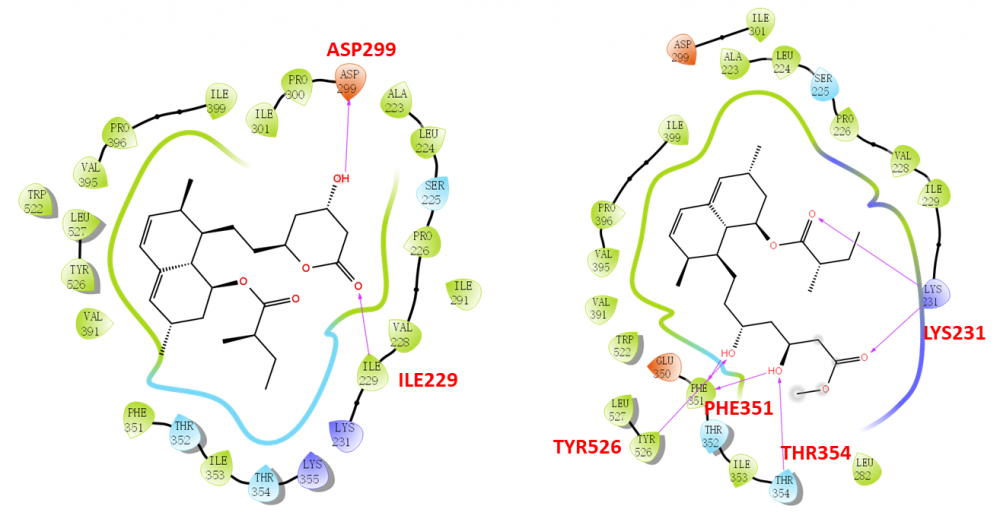
ABSTRACT
Ten secondary metabolites were isolated from cultures of the marine coral-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus SCSIO41404. The compounds were identified as monacolin K (1), methyl ester of lactone ring-opened monacolin K (2), asperterreusine C (3), 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde (4), 4-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl) benzaldehyde (5), kojic acid (6), p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid methyl ester (7), o-hydroxyphenylacetic acid methyl ester (8), N-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-acetamide (9), and (S)-methyl 2-acetamido-3-phenylpropanoate (10), by comparing the spectroscopic data with the reported literature values. They were evaluated for their cytotoxic, antibacterial, and enzyme (pancreatic lipase and acetylcholinesterase) inhibitory activities. Monacolin K (1) and its derivative (2) were revealed with obvious pancreatic lipase (PL) inhibitory effects. The in silico molecular docking with PL protein was further performed to understand the binding effects, and it is suggested that the ring opening of the monacolin K facilitates for the PL inhibitory activities.
KEYWORDS- Coral-derived fungus
- Aspergillus terreus
- secondary metabolites
- pancreatic lipase
- molecular docking