JOURNAL 2984
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2024 Issue: 2 March-April
p.220 - 236
Viewed 2320 times.
-
Elmakaoui Abdellah

-
Houda Damour

-
Ilhame Bourais

-
Bouabid Badaoui

-
Imtara Hamada

-
Mahmoud Tarayrah

-
Omar Noman

-
Asmaa Oubihi

-
Karima El Kabous

-
Souad El Hajjaji

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
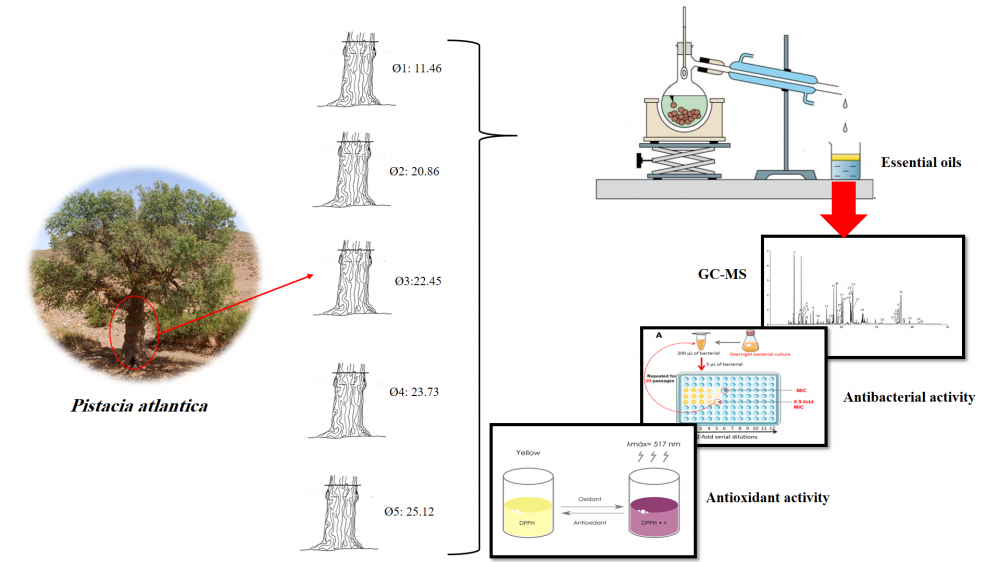
The aim of the present study is to assess the chemical compounds, antibacterial potential, and antioxidant qualities of essential oils as extracted from dried leaves of five Pistacia atlantica of different trunk diameters from Rommani (a rural area in the west of Morocco). The DPPH and FRAP methods are used to measure antioxidant activity. Essential oils have been tested on Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter cloacae, Klebsiella pneumonia, Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus epidermidis. The essential oils were analysed using gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC/MS) analysis. The obtained results show that the tree's diameter, which is proportional to its age, was related to the original components. Terpinen-4-ol (19.00%–22.33%) with a diameter greater than or equal to 23.73 cm and α-Pinene (18.49%–37.51%), smaller than or equal to 22.45cm, are the two primary components. The findings of the DPPH and FRAP tests indicate that the IC50 values range from 8.70 ± 0.02 mg/mL to 11.46 ± 0.01 mg/mL and the EC50 values range from 8.27 ± 0.04 mg/mL to 12.76 ± 0.16 mg/mL, respectively. The interval of the zone of inhibition [8.77 ± 1.48 mm – 12.07 ± 2.51 mm], according to the results of antibacterial activity testing, shows that MIC and MBC vary between 4 and 10 µL/mL.
KEYWORDS- P. atlantica
- DPPH
- chemical compounds
- antibacterial activity
- secondary metabolites
- biological activity