JOURNAL 3217
Records of Natural Products
Available Online: July 01,2024
p.1 - 17
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.466.2404.3217 (DOI number will be activated after the manuscript has been available in an issue.)
Viewed 251 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
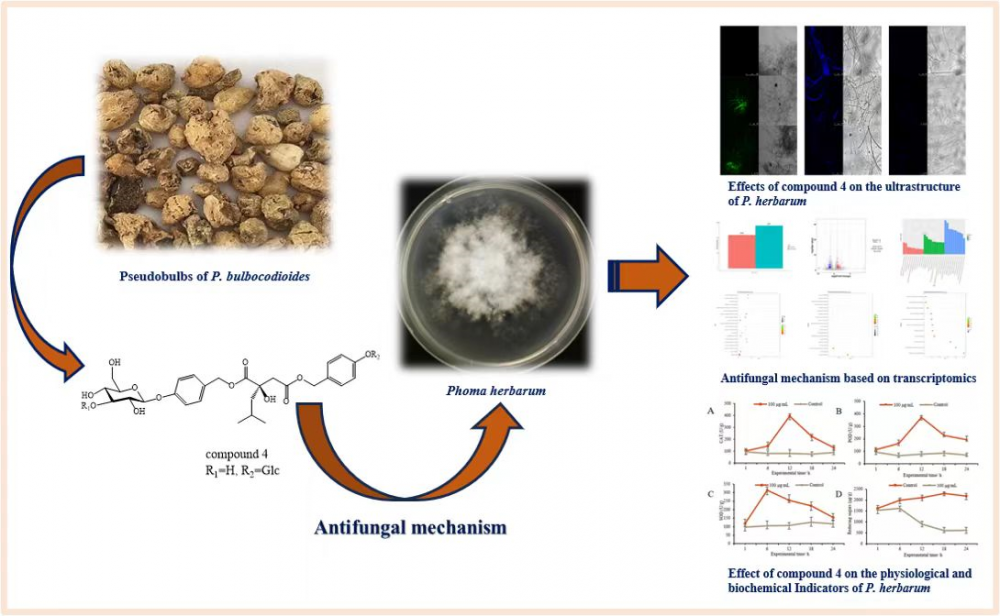
ABSTRACT
The bioactive compounds of the pseudobulbs of Pleione bulbocodioides were isolated, purified, and identified using modern spectroscopic techniques, which identified seven butanedioic acid compounds. Compounds 1-3, 5, and 6 were isolated for the first time from Pleione bulbocodioides. The antifungal activity of the seven compounds was evaluated through cytotoxic activity assays, revealing that compound 4, militarine, exhibited moderate inhibitory activity against Phoma herbarum, with an effective concentration (EC50) of 68.575 μg/mL. We get further deep insight into the antifungal mechanism of militarine against Phoma herbarum through electron microscopy, transcriptomics, and changes in physiological and biochemical indicators. Transcriptomic sequencing revealed 216 significantly upregulated differentially expressed genes and 277 significantly downregulated differentially expressed genes. Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis showed that differentially expressed genes were involved in pathways related to secondary metabolism, biosynthesis, membrane components, nitrogen metabolism, and ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter, suggesting that militarine may inhibit the normal growth of hyphae through these pathways.
KEYWORDS- Pleione bulbocodioides
- Phoma herbarum
- chemical composition
- antibacterial mechanism