JOURNAL 2605
Organic Communications
Year: 2022 Issue: 4 October-December
p.346 - 355
Viewed 2604 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
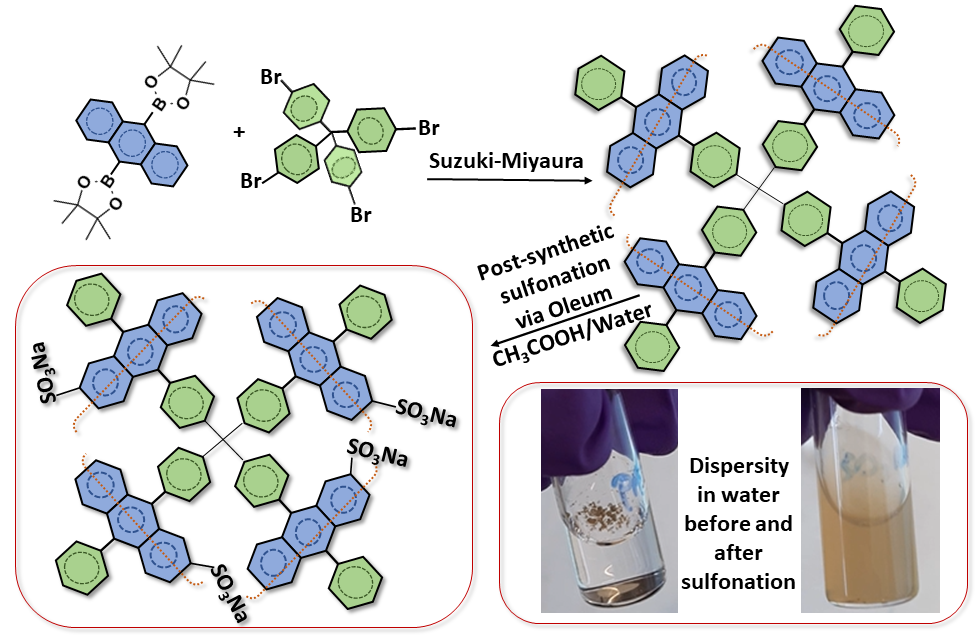
ABSTRACT
Post-synthetic modification is an alternative pathway to introduce functionalities into the backbone of porous materials. Sulfonation of porous organic polymers is one of the frequently applied post-functionalization since the sulfonate groups are interesting for various applications such as carbon dioxide storage, proton conduction, ion removal. Moreover, sulfonation drastically improve hydrophilicity of the hydrophobic materials, therefore, makes the final compounds more processable in aqueous media. In this article, a procedure for post-synthetic sulfonation of a diphenylanthracene (DPA) based porous aromatic framework (DPA-PAF) is presented. Oleum (fuming sulfuric acid) was used as the sulfonation agent in acetic acid+water media instead of the conventionally used chlorosulfonic acid in the chlorinated solvents. Aside from macroscopic (visual) observations such as improved dispersibility in water when compared to the parent compound, the introduction of sulfonate groups was confirmed by using infra-red spectroscopy, elemental analysis, and gas sorption (surface area) measurements.
KEYWORDS- Porous organic polymers
- porous aromatic frameworks
- PAF-1
- post-synthetic modification
- sulfonation
- oleum