JOURNAL 3719
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2026 Issue: 3
p.2 - 2
Viewed 12 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
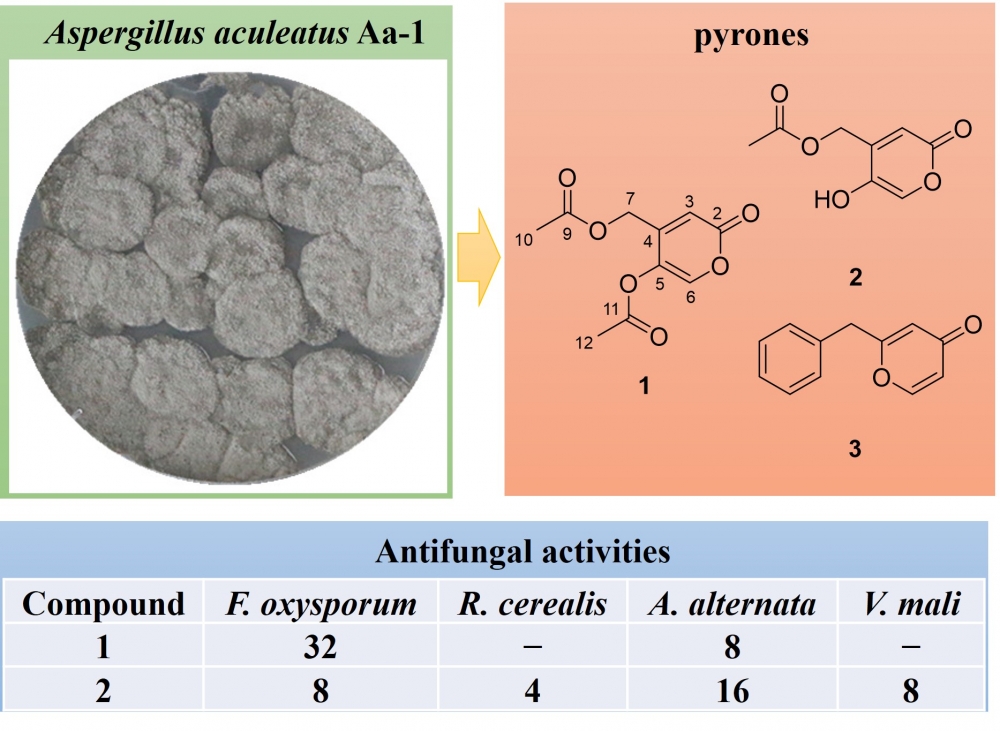
This paper presents a chemical study of the tobacco-derived fungus Aspergillus aculeatus Aa-1. Three pyrones including a new α-pyrone namely asperacuone A (1), the α-pyrone saadamycin (2), and the 2-benzyl-γ-pyrone (3) were isolated from the EtOAc extract of this fungal strain. The chemical structures of these compounds were precisely determined via nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1D/2D NMR) as well as high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HRESIMS). The antifungal activities of compounds 1–3 were then evaluated against six agricultural pathogenic fungi. While compound 1 revealed strong inhibitory potency against Alternaria alternata (minimum inhibitory concentration [MIC] = 8 μg/mL), compound 2 showed broad-spectrum inhibitory activities against the tested pathogens (MIC = 4–16 μg/mL)
KEYWORDS- Tobacco-derived fungus
- Aspergillus aculeatus
- secondary metabolite
- α-pyrone
- antifungal activity