Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Reports
Year: 2018 Volume: 1 Issue:1 January-December
1) Welcome to the first issue of BioorgMedChemRep for 2018!
2) Immunomodulation of macrophages for bone formation

Especially in elderly women osteoporosis leads to decline in the strength of the bone tissue by erosion of its mass. Weakened bone tissue is more prone to breaks. Patients mostly realize this situation after having a bone breakage especially with the wrist and hip fractures. There has not been an effective way of improving this debilitating condition. A new approach aiming to regulate the activities of the immune system cells in order to reverse osteoporosis and push the tissue for the formation of the bone structure gained attention due to its promising potential. In this review, I will be focusing on this approach by regulation of the macrophage activity, the major immune cell type that is involved in the bone formation. Immunomodulation of the macrophages enable formation and healing of the bone tissue in the patients and conducting more studies in this area would certainly improve the quality of the applicable medicines.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.11.18.09.899 Keywords Macrophages immunomodulation bone bone formation osteoporosis immunomodulatory agents DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2018 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) The synthesis of two novel bicyclic haloketones and measurement of their biological activity
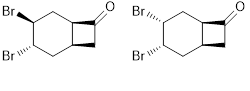
The electrophilic addition of bromine to bicyclo[4.2.0]oct-3-en-7-one in CHCl3 at 0 °C led to 60% yield of trans- and 30% yield of cis-dibromide. The structure of the synthesized molecules was determined using 1H and 13C NMR spectra. The biological activity of cis- and trans-dibromide was investigated in terms of antibiotic and toxic effects at cellular level using microbiologic and cytogenetic test, respectively. The antimicrobial activity of trans-dibromide9 and cis-dibromide10 was tested against Bacillus spizizenii ATCC 6633, Salmonella typhimurium ATCC 14028,Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027. Peripheral blood lymphocytes culture assay was used for determining the cytotoxicity of trans-dibromide 9 and cis-dibromide 10 substrates. Cis- and trans-dibromide showed antibiotic activity and the toxic effects of cis- and trans-dibromide were measured at cellular level by mitotic index as the cell kinetic parameter in a peripheral lymphocyte culture assay.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.12.18.11.1035 Keywords Dibromoketone biological activity antibiotic effect toxic effect mitotic index DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2018 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Citric acid synthesis efficiency of Aspergillus niger in carob molasses based media

Citric acid is an inactive ingredient that is widely used in pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food industries. It is an organic acid that is produced during the Krebs cycle of the cell metabolism therefore it is present in the living organisms. Natural resource of the citric acid is citrus fruits and it is well known for its preservative action. Synthetically by utilizing from biotechnological tools, it can be produced by Aspergillus niger in a media that can supply the sµgar source. In this study we compared the efficiencies of carob molasses and potato based broths to grow A. niger for citric acid production. Carob molasses are widely found in the region and their utilization as media in biotechnological production of the citric acid would be advantageous. Our results support that this media can be used as an efficient source for the citric acid producing fungus A. niger in the bioreactors.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.15.18.12.1124 Keywords Microbiology Biotechnology Citric acid Carob Pharmaceutical industry Cosmetics DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2018 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Electrochemical studies of regorafenib in non-aqueous media

A novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor, regorafenib was electrochemically studied using a GC disc electrode in non-aqueous media. A well-resolved, irreversible, diffusion-controlled oxidation peak was obtained at 1.55 V in acetonitrile solution containing 0.1 M TBAClO4. Experimental conditions such as scan rate, indicate that two electrons play a role in the electrochemical oxidation of regorafenib. The recommended method was successfully applied to the determination of regorafenib in drug capsules.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.10.18.12.110486 Keywords Regorafenib cyclic voltammetry electrochemical oxidation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2018 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Analyzing of some drugable properties of hydrazono-pyridazinones
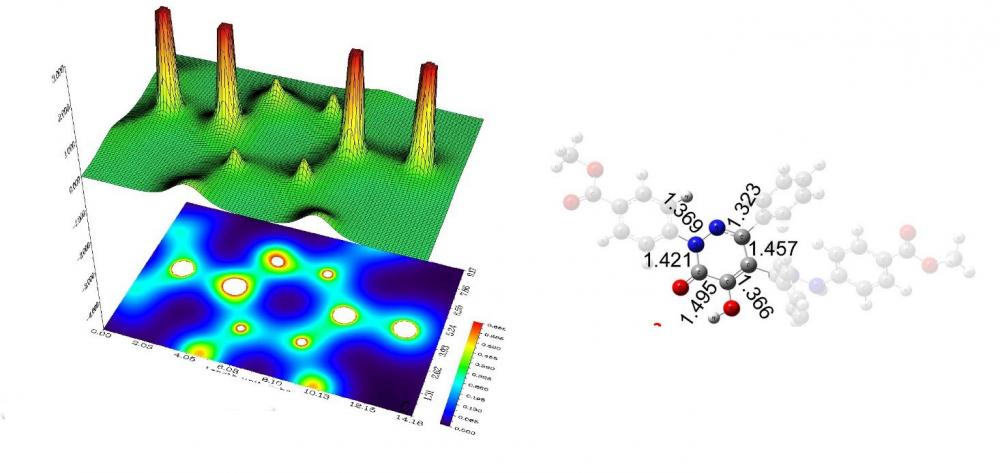
Some pyridazinones with ortho hydroxy hydrazone were investigated using DFT/B3LYP 6-311 G(d,p) method. Optimized molecules were taken account for NBO analysis by using DFT/B3LYP 6-311+G(d,p) method and information gained NBO analysis gave some important point for predicton of polarization of atoms. Furthermore, electrostaticpotential surfaces (MEP) were calculated and visualized in order to predict charge distribution as well as the shape/volume of the surface of the pyridazinones. HOMO-LUMO orbitals were computed and with these information hardness, electronegativity and global electronegativity index were calculated. For aromaticity of pyridazinone ring HOMA, BIRD and NICS indexes were calculated and aromaticity indexes revealed that which heterocyclic ring was the most aromatic and stable against metabolization effect of enzymes. Electron density map with projection for 2 was plotted and its localization of electron density was discussed. Lipinski’s rule of five was calculated for investigated molecules for prediction of oral uptake and drug candidates.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.10.18.12.1104 Keywords Pyridazinone aromaticity NBO Analysis physicochemical properties drug design DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2018 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.