Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Reports
Year: 2019 Volume: 2 Issue:1-2 (January-December)
1) Targeting mTOR: up-to-date mTOR inhibitors
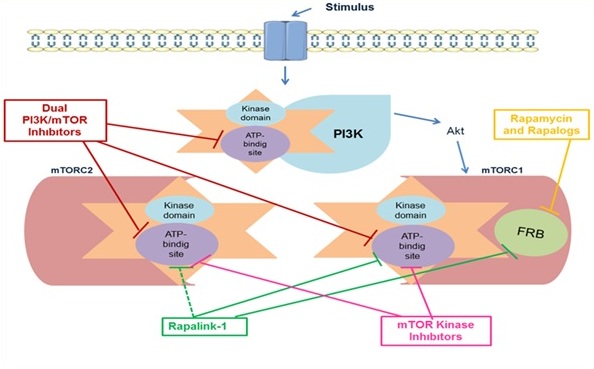
mTOR, a member of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase family, controls major physiological cellular processes such as growth and metabolism in response to nutrients, growth factors, and cellular energy levels. Furthermore, deregulation of the mTOR activity has been associated with various pathological conditions such as cancer, diabetes, obesity, neurological diseases, and genetic disorders. Therefore, research on the mTOR signalling pathway and the development of effective molecules on this pathway has been continuing intensively in recent years. In the past decade, numerous mTOR inhibitors have been developed and many are currently in clinical trials. These molecules are classified as Rapamycin and its analogs (all are termed rapalogs), ATP-competitive dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors, mTOR kinase inhibitors, and Rapa Links. In this review, we aimed to summarize current findings on mTOR signalling network and molecules acting on this signalling pathway.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.16.19.09.1417 Keywords mTOR mTOR inhibitors rapalogs dual inhibitors kinase inhibitors rapaLinks DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Determination of solifenacin succinate in human plasma and pharmaceutical formulations using HPLC-UV
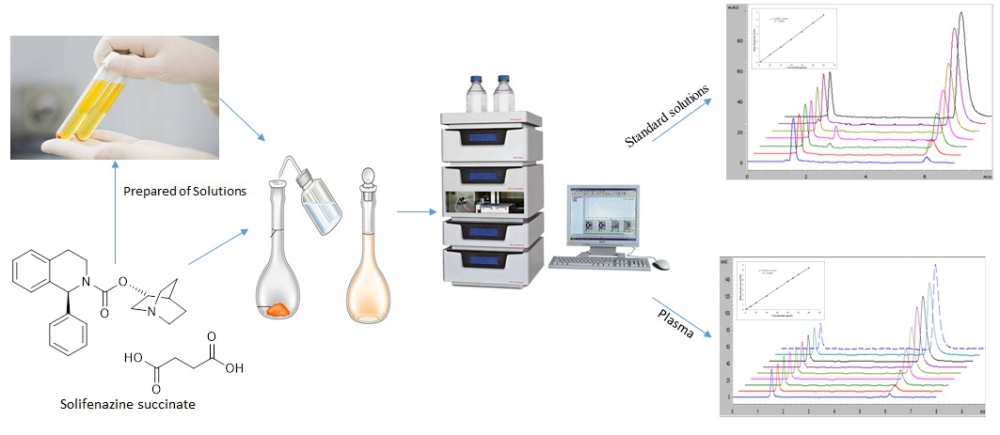
An accurate, rapid and precise high performance liquid chromatographic coupled with ultraviolet detector method has been developed for the determination of solifenazine succinate in pharmaceutical preparation and human plasma. Quantitative analysis of solifenazine succinate was performed using a C18 column at wavelength at 210 nm. The mobile phase consisted of 10 mM ammonium formate buffer (pH 4.0), acetonitrile and methanol (52.5:32.5:12.5 v/v/v). The method showed linearity in the concentration range of 3-60 μg/mL and the correlation coefficient was 0.9998 and 0.9994 for the standard and human plasma solutions, respectively. The proposed method was within acceptable limits in terms of accuracy, precision, selectivity, linearity, sensitivity and recovery parameters. This method is readily applicable for the determination of solifenazine succinate in human plasma and pharmaceutical preparations.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.17.19.10.1451 Keywords Solifenacin succinate pharmaceutical formulations human plasma HPLC DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Synthesis and biological evaluation of substituted hexahydroquinoline derivatives
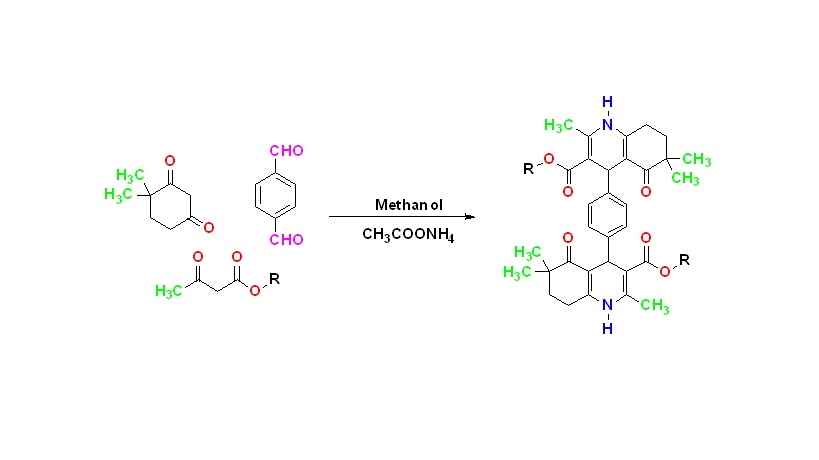
It is known that microorganisms develop resistance to the drugs used in the treatment of diseases caused by bacteria and fungi. Therefore, the discovery of new drug molecules have great importance for the treatment of these diseases. In this study, compounds having dialkyl 4,4'-(1,4-phenylene)bis(2,6,6-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate) general structure which are expected to exhibit antibacterial and antifungal activity were synthesized. 1H-NMR and IR analyzes were performed to prove their structures. All compounds were tested against Gram (+) Staphylococcus aureus and Gram (-) Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa to evaluate their in vitro antibacterial activity; Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii to evaluate in vitro antifungal activity. According to the biological activity data, the most active derivative in the series was compound 2 as an antibacterial agent and compound 7 as an antifungal agent.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.bmcr.18.19.11.1483 Keywords hexahydroquinoline Hantzsch synthesis antibacterial antifungal inhibition DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Synthesis and biological evaluation of some 4-amino-3-mercapto-1,2,4-triazoles bearing mannich base
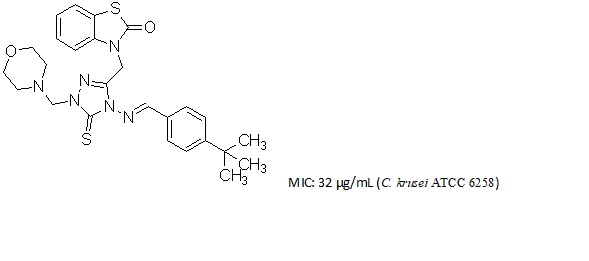
Bacterial and fungal resistance to almost all antimicrobial agents have been observed in disease causing bacteria and fungi. A series of 3-({4-[substitutedbenzylideneamino]-1-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-5-thioxo-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl}methyl)-2(3H)-benzothiazolone (6a-6g) were prepared by the reaction of morpholine in the presence of formaldehyde using microwave irradiation with the yield ranging from 50% to 98%. The newly synthesized compounds were characterized on the basis of elemental analysis, IR and 1H-NMR. All the synthesized compounds were tested for their antibacterial activities against Gram + and Gram – bacteria, their clinical isolates and antifungal activities against Candida species in vitro. Many of these compounds exhibited potent antifungal activity, while compound 6g (MIC:32 µg/mL) had comparable activity with ampicillin and gentamycin (MIC: 4 µg/mL) against E.faecalis isolate.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.bmcr.19.19.12.1498 Keywords 5-Substituted-4-amino-3-mercapto-1,2,4-triazoles 2(3H)-benzothiazolone Mannich base antibacterial antifungal MIC DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.