Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Reports
Year: 2020 Volume: 3 Issue:2 July-December
1) Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1,3,5-triazine-substituted ureido benzenesulfonamides as antioxidant, acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors
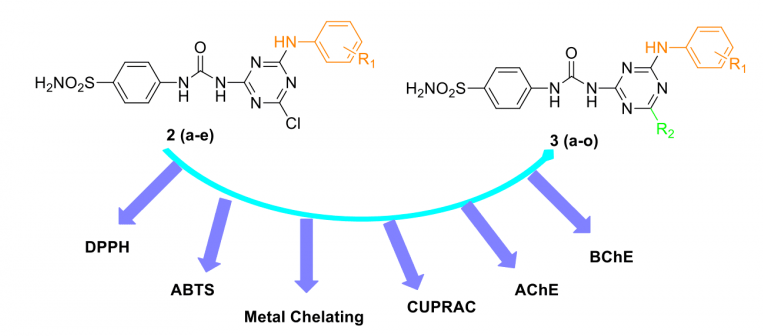
A series of twenty 1,3,5-triazine-substituted ureido benzenesulfonamides 2 (a-e) and 3 (a-o) were re-synthesized and assayed for antioxidant properties by using several different methods including 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl hydrazyl (DPPH) free radical scavenging assay, 2,2′-azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) cation radical decolarization assay, metal chelating and cupric reducing antioxidant capacity (CUPRAC) methods. The inhibitory effects of compounds on acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) enzymes have been also demonstrated. All compounds showed a greater antioxidant capacity against ABTS assay by having a more potent activity than the standards BHT, BHA and α-TOC. In general, all compounds were non susceptible to against AChE enzyme. On the other hand, several lead compounds were obtained from the current series against BChE enzyme. More specifically, compound 3m showed great inhibition profile against BChE with % inhibition value of 93.77, which is better than the standard drug galantamine (% inhibition value of 87.86).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.bmcr.22.20.07.1706 Keywords 1,3,5-triazine; sulfonamide acetylcholinesterase butyrylcholinesterase antioxidant DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) New molecule design with in-silico methods for Covid-19 treatment
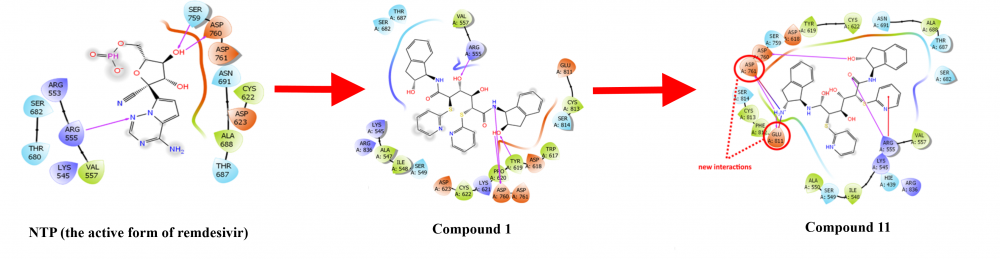
Intensive studies are being conducted to develop effective prevention and treatment strategies for the Covid-19 pandemic. During a pandemic, it is vital to act quickly to develop a defense strategy. It usually takes a long time to develop a preventive vaccine, and immediate drug development is needed to reduce the impact of the rapidly increasing Covid-19 pandemic. This study aimed to design an effective and potent drug by selecting remdesivir, a nucleotide analog prodrug that inhibits viral RNA polymerases and is known to be active against Covid-19. Remdesivir is metabolized into active nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) by the host; this metabolite competes with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) for incorporation into the nascent RNA strand. Therefore, molecular docking studies have been conducted based on NTP (the active form of remdesivir), and a target molecule that could be effective against Covid-19 has been designed.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.bmcr.23.20.08.1773 Keywords SARS-CoV-2 , Covid-19 remdesivir molecular docking DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.