Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2021 Volume: 15 Issue:2 July-December
1) Characterization of low-density polyethylene reference material for melt flow rate by collaboration of NIS and a network of competent laboratories
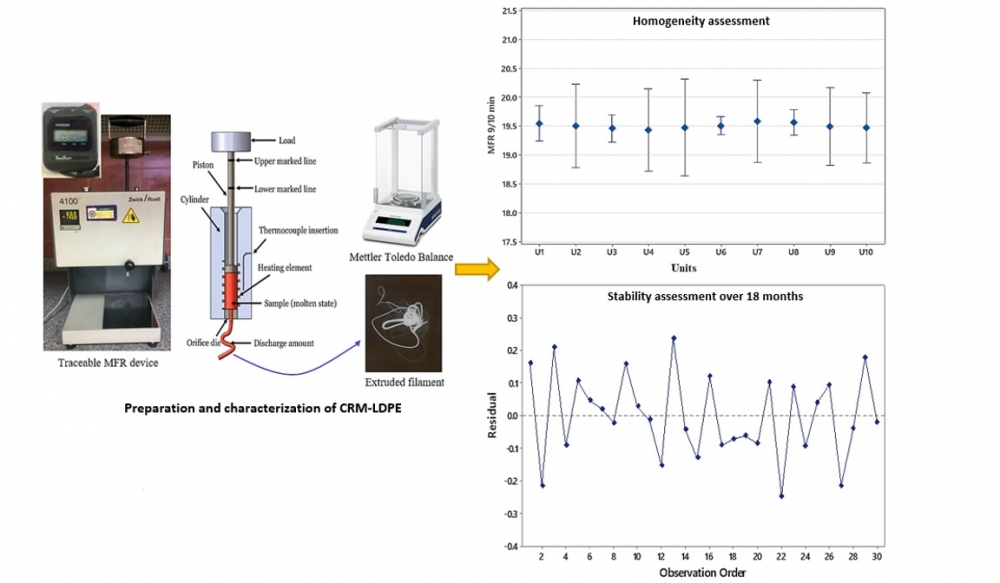
The growth rate of plastic manufacturing all over the world and in the middle east as oil producing countries increased the rate of thermoplastics production and the needs of reference materials (RMs) for use in performance evaluation of measuring instruments and ensuring validity of measurement results. This article was focused on the preparation of RM based melt mass-flow rate from low-density polyethylene (LDPE) according to ISO 1133-1 standard. The characterization was evaluated from around 10% of prepared units, then the samples were distributed to a network of collaborating laboratories in order to ensure the validity of the RM production process. The value of melt mass-flow rate of LDPE was determined to be 19.51 g/10 min under a temperature of 190℃ and a load of 2.16 kg with expanded uncertainty 0.38 at 95% confidence level. The obtained values were confirmed from the data reported by the network of collaborating laboratories.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.63.2107.2148 Keywords Reference material melt mass-flow rate LDPE ISO 1133-1 homogeneity and stability collaborative study DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Development of a quality control material for the analysis of volatile compounds in alcoholic beverages
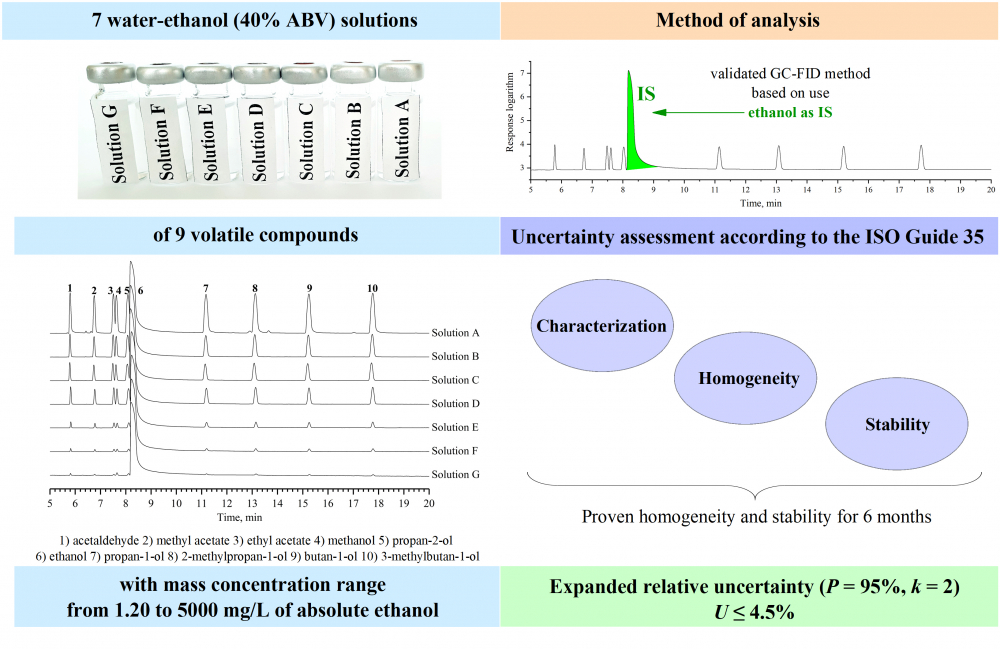
A quality control material (QCM) for the analysis of volatile compounds in alcoholic beverages was developed. The problems of the development and production of QCM were investigated. The seven water-ethanol solutions, containing 9 volatile compounds (acetaldehyde, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate, methanol, propan-1-ol, propan-2-ol, 2-methylpropan-1-ol, butan-1-ol and 3-methylbutan-1-ol) with a concentration range from 1.20 to 5000 mg/L of anhydrous ethanol were prepared and studied according to the ISO Guide 80 and ISO Guide 35 in order to prove their stability over 6 months. The algorithm for the assessment of uncertainty associated with the characterization of QCM was developed. The studies were carried out by validated direct gas chromatography (GC) method with flame ionization detection (FID), based on using ethanol as an internal standard. The expanded relative uncertainty of QCM does not exceed 4.5 %.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.66.2111.2259 Keywords Quality control material (QCM) homogeneity assessment stability assessment alcoholic beverages volatile compounds uncertainty estimation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Simultaneous estimation of Pyridoxine HCl and FMOC-Leucine using derivative and chromatographic approach in pharmaceutical dosage form
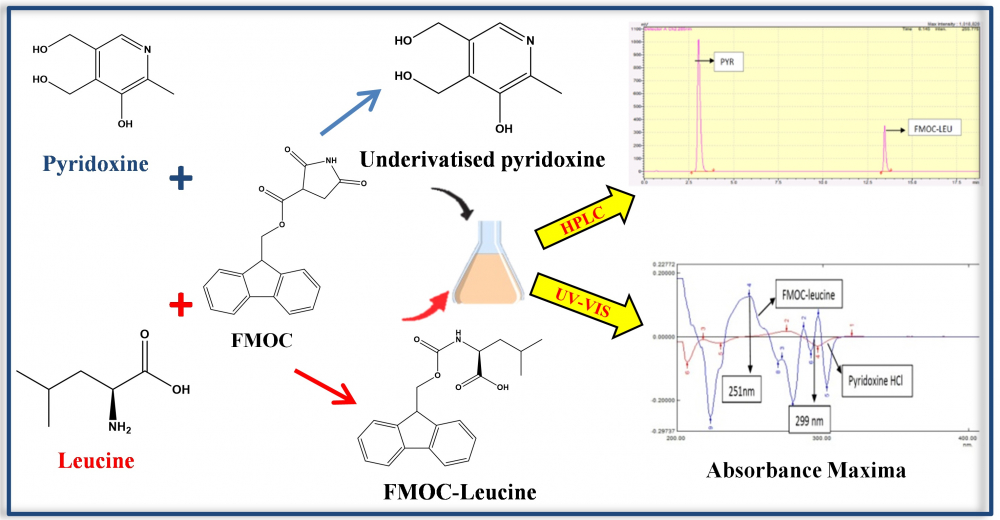
This work developed a fast and simple method for quantifying two important amino acids, Pyridoxine Hydrochloride and Leucine, to treat obesity. In the current study, the active hydrogen of a free amino group at Leucine was only replaced by non-polar group using N-(9-Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyloxy) succinimide (FMOC-OSU) as a derivatizing agent, resulting in conversion of Leucine to FMOC-Leucine derivative to make an analyte less reactive, volatile, and thus improve its chromatographic behavior. The aim of the present study is to develop accurate, precise, and selective first order UV-Visible spectroscopic and HPLC methods for the simultaneous estimation of Leucine and pyridoxine HCl and to validate these methods as per International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) Q2 (R1) guidelines. In the developed method the correlation co-efficient was found to be 0.999; 0.999 and 0.995; 0.997 for FMOC-leucine and pyridoxine HCl respectively. The %RSD for accuracy was found to be less than 2. The detection limit and quantification limit for validation in UV-Visible spectroscopy and HPLC for Pyridoxine HCl and FMOC-Leucine were found under limit. The methods were also found to be precise and robust (% RSD= < 2%) and % assay of the marketed formulation containing both the drugs was found to be 98.6%; 98.7%; 99.2%; 99.3% for Pyridoxine HCl and FMOC-Leucine respectively. Comparison between both the methods was done by one-way ANOVA using % assay values. There was not any significant difference found. Both the methods can use for simultaneous estimation of Leucine and Pyridoxine HCl.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.65.2109.2205 Keywords Pyridoxine HCl FMOC-Leucine derivatization UV-visible spectroscopy HPLC validation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) LC-HRMS profiling of phytochemicals, antidiabetic, anticholinergic and antioxidant activities of evaporated ethanol extract of Astragalus brachycalyx Fischer

Astragalus is a perennial plant that has existed for about 2500-3000 years and consists of more than 250 taxonomic parts. Twenty species of Astragalus are endemic to Turkey, as well as the richest genus with 425 taxa. The roots of Astragalus species are used in folk medicine as hepatoprotective, antioxidant, antibacterial, antihypertensive, antidiabetic and diuretic. Also, it is used to treat diabetes mellitus, leukemia, nephritis and uterine cancer. It is known that in Anatolia, Astragalus roots are traditionally used against leukemia and wound healing. For the purpose, the measuring of antioxidant activity of evaporated ethanol extract of Astragalus brachycalyx FISCHER (EEAB), some bioanalytic methods including DPPH• and ABTS•+ scavenging effects, ferric ions (Fe3+) and cupric ions (Cu2+) reducing abilities, and metal (Fe2+) chelating activity were realized. α-Tocopherol, ascorbic acid, and BHT were used as the standard antioxidants. On the other hand, some phenolic compounds, which responsible for antioxidant activities of EEAB was determined by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS). At the similar concentration, EEAB exhibited efficient antioxidant effects when compared to standard compounds. Additionally, EEAB showed IC50 values of 1.985 μg/mL toward acetylcholinesterase (AChE), 0.620 μg/mL on α-glycosidase and 0.306 μg/mL against α-amylase enzymes.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.62.2107.2155 Keywords Astragalus brachycalyx phenolic compounds antioxidant activity acetylcholinesterase α-glycosidase α-amylase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Quantification of antileukemic drug Dasatinib in human plasma: Application of a sensitive liquid chromatographic method

Dasatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that is approved and prescribed to patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia and Philadelphia chromosome. Present work reports development of reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatographic method for determination of Dasatinib in human plasma and validation of the developed method according to the guidelines provided by European Medicines Agency (EMA). An RP-HPLC method with UV detection and isocratic elution has been developed and validated for analysis of Dasatinib in human plasma over a range of 5-300 ng/mL. Imatinib was used as an internal standard. Both, the drug and the internal standard were separated on the Inertsil C18 column (150 mm×4.6 mm×0.005 mm) using Ammonium Acetate buffer pH 6.4 and acetonitrile at a ratio of 65:35 as mobile phase. The flow rate was adjusted to 0.7 mL min-1. The detection was performed at 310 nm wavelength. Sample pre-purification was performed through simple protein precipitation using acetonitrile followed by sample collection through centrifugation. The developed method was linear in the range of 5-300 ng/mL with correlation coefficients (r2) of 0.995. The lower limit of quantification for Dasatinib in plasma was 5 ng/mL. The accuracy and precision of the method were well within the acceptable limits of 15% over the linear range. In general, the developed method is efficient and inexpensive. It is very simple from the extraction of drug from the plasma matrix to the isocratic elution of analytes. From the data, it can be concluded that the developed method is selective, precise and accurate and applicable for the determination of Dasatinib in human plasma samples.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.64.2108-2174 Keywords Dasatinib human plasma liquid chromatography method validation UV DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Development of a quick reverse phase liquid chromatographic method with photodiode-array detection for quantitative determination of chlorthalidone, metoprolol succinate and telmisartan in tablet formulation

A quick and simple reversed-phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic method (RP-HPLC) with isocratic elution has been developed and validated for the concurrent quantitative determination of chlorthalidone, metoprolol succinate and telmisartan in the bulk mixture and tablet dosage form. The chromatographic separation was performed using Inertsil Octadecyl-Silica (ODS- C18) Column (150mm×4.6mm, 5μm) stationary phase. The separation and elution was carried out using a mobile phase mixture of phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 2.5) and acetonitrile at a ratio of 40:60 v/v and 0.7 mL/min flow rate. Chlorthalidone, metoprolol succinate and telmisartan were eluted at 2.96±0.5 min, 4.31±0.5 min and 5.94±0.5 min respectively. The response was recorded using a photodiode array (PDA) detector at 225 nm wavelength. The selected method was linear in the range of 3.21-18.72 µg/mL, 6.25-37.50 µg/mL and 10-60 µg/mL while percentage recovery was in the range from 99.15 to 99.93%, 99.15 to 99.42% and 100.03 to 100.08% for chlorthalidone, metoprolol succinate and telmisartan respectively. The method was found to be sensitive, selective, linear and reproducible and the results obtained suggest the suitability of the developed method for routine analysis of the formulations containing the combination of these drugs.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.6012106.2098 Keywords Chlorthalidone high-performance liquid chromatography metoprolol Succinate telmisartan validation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Isolation of amygdalin epimer at high diastereomeric purity and its structural characterization by spectroscopic and Q-TOF LC-MS methods
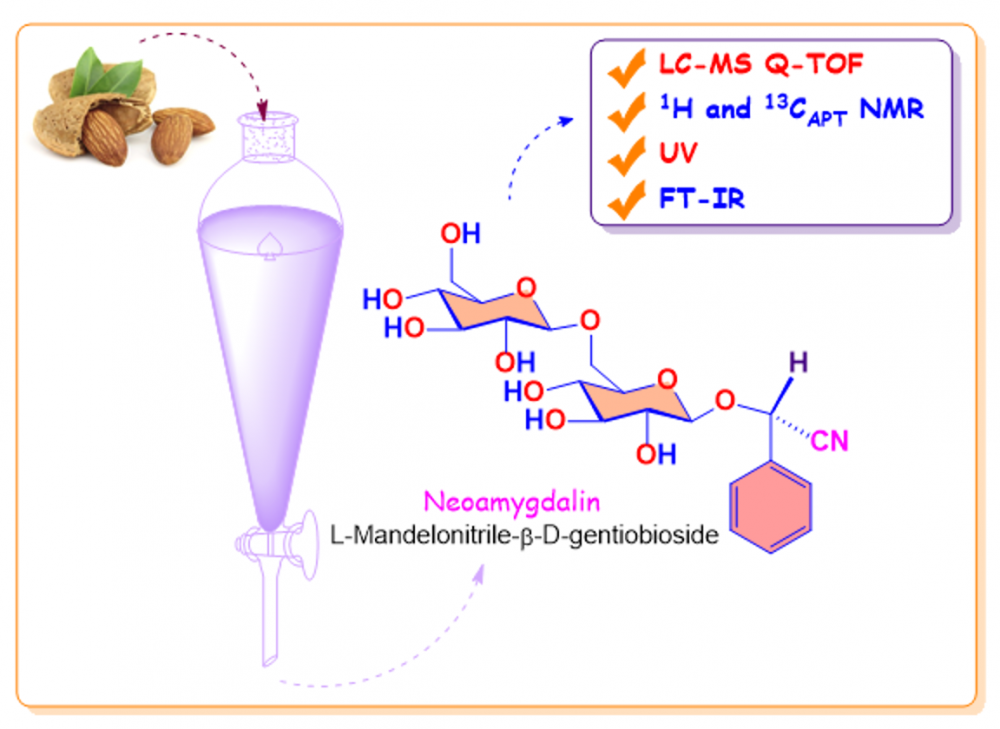
Amygdalin, a cyanogenic glycoside mostly found in the bitter almond kernel, plays an important role in conventional and modern medicine applications. The high diastereomeric purity amygdalin was isolated with chromatographic purification methods and recrystallization. Amygdalin and neoamygdalin were separated chromatographically using the porous graphitic carbon column. Identification and confirmation of each molecule was performed with the ESI Quadrupole Time of Flight system coupled with a reversed phase LC.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.60.2105.2076 Keywords Amygdalin neoamygdalin cyanogenic glycoside LC-MS Q-TOF chromatography DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
