JOURNAL 1336
Organic Communications
Year: 2019 Issue: 3 July-September
p.132 - 142
Viewed 4286 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
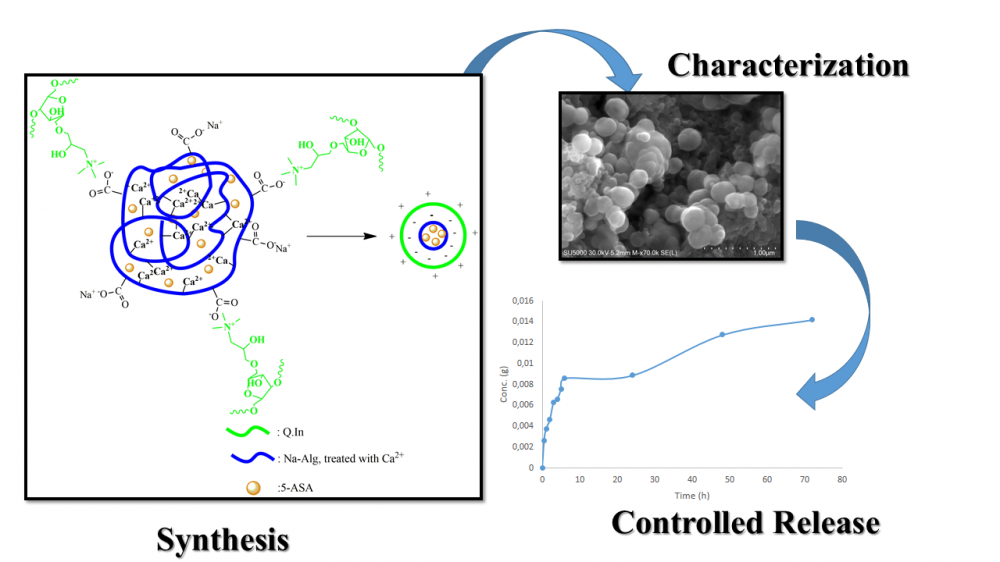
ABSTRACT
Protection of drug molecules from digestive enzymes and providing their controlled release at the site of intestinal inflammation are the most important aims of oral nano drug delivery systems (NDDSs). Encapsulation and controlled release of 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), which is a well-known anti-inflammatory drug, for effective treatment of Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) were aimed in this study. For the preparation of core-shell structured NDDSs, 5-ASA loaded sodium alginate (Na-Alg) cores with negative surface charge were prepared by calcium chloride crosslinking of Na-Alg and subsequently coating with quaternized inulin (QIn) via Coulomb interaction. As a shell layer, QIn was separately synthesized by quaternization of inulin with glycidyl trimethylammonium chloride (GTMAC). While the crosslinked Na-Alg core is responsible for the protection of 5-ASA from acidic pH in stomach, quaternized inulin shell, known to be highly mucoadhesive, was implemented for digestion by the intestinal flora providing controlled release of 5-ASA at inflammation site of small and/or large intestine. Characterization of NDDSs was carried out using GPC, FT-IR, 1H-NMR and SEM techniques. Ideal slow release of 5-ASA was obtained with the from spherical particles having core and shell sizes of 84-100 and 156-198 nm, respectively.
- Inulin
- Sodium Alginate
- Nano-Hydrogel
- Oral Delivery
- 5-ASA
- Controlled-Release