JOURNAL 2257
Organic Communications
Year: 2021 Issue: 4 October-December
p.323 - 333
Viewed 2792 times.
-
Reddi Mohan Naidu Kalla

-
Lachhireddy Venkataramana

-
Chintha Venkataramaiah

-
K. Swetha Kumari

-
Mavallur Varalakshmi

-
Chamarthi Naga Raju

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
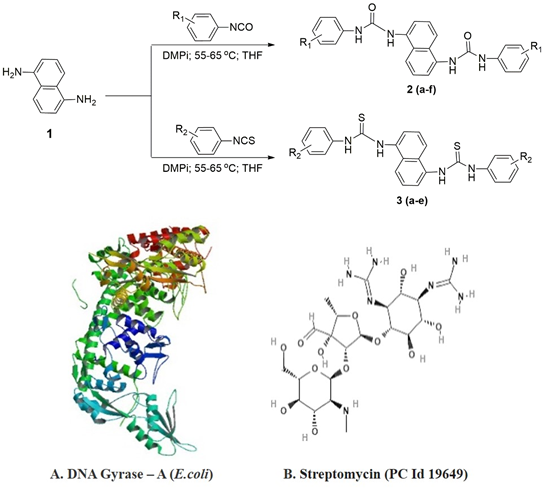
A pioneering class of urea/thiourea derivatives of naphthalene-1,5-diamine was synthesized in excellent yields (89-96%) by one-pot procedure via treatments with phenyl isocyanates or phenyl isothiocyanates. All the constructed derivatives were evaluated for antimicrobial activity using in vitro and in silico methods. The obtained results showed that, all the titled compounds displayed the most significant antibacterial activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria namely B. substilis, B. sphaerius, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, K. aerogenes, C. violaceum and antifungal activity against A. Niger, C. tropicum, R. oryzae, F. moniliforme and C. lunata when compared with the standard drugs such as ciproflaxacin and clotrimazole. Among all, the compounds 2c, 2e and 3d, 3e displayed higher content of antimicrobial activity akin to the rest of the compounds due to the presence of fluoro substitution on aromatic ring. Furthermore, molecular docking studies provided support to the in vitro studies. Four of the synthesized compounds, 4-fluorophenyl, 3-trifluoromethylphenyl, 4-chlorophenyl exhibited significant binding modes and were the best target ligands as they fitted more stably into the DNA gyrase binding pocket. Henceforth, it is suggested that, the fabricated urea/thiourea derivatives of naphthalene-1,5-diamine would stand as the prosperous antimicrobial drug candidates for further studies.
KEYWORDS- Naphthalene-1,5-diamine
- antibacterial Activity
- DNA Gyrases
- urea/thiourea derivatives