JOURNAL 2388
Organic Communications
Year: 2022 Issue: 2 April-June
p.204 - 211
Viewed 2610 times.
-
Abbas Khaja Mohideen

-
Kasim Mohammed Mustaque

-
Ismail Salim Meeran

-
Annadurai Subramani

-
V. S. Jamal Ahamed

-
Habeebullah Thajudeen

-
Timiri Khudus Shabeer

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
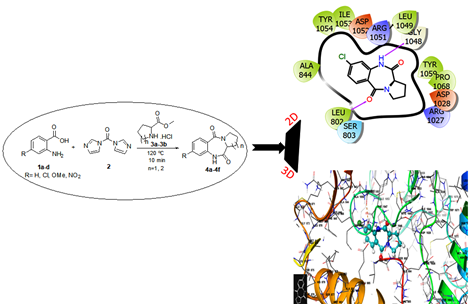
ABSTRACT
he reaction of anthranilic acid with proline or pipecolinic methyl ester hydrochloride in presence of 1,1’-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) on oil bath heating under solvent-free condition afforded 1,4-benzodiazepine-2,5-dione (BZD) derivatives in moderate to good yields. Operational simplicity, absence of hazardous solvents, utility of an inexpensive coupling reagent (CDI) and mild reaction conditions are the significant advantages of this methodology. The cytotoxic activity of six BZDs were evaluated against HCT15 (Human Colon adenocarcinoma), SKMel2 (Human Skin Melanoma) and SKOV3 (Human Ovarian adenocarcinoma) cell lines. Compound 4b with para substituted chlorine atom showed moderate cytotoxicity against HCT15, SKMel2 and SKOV3 with IC50 values 37.04 ± 1.13, 39.45 ± 0.77 and 36.61 ± 0.10 µg/mL respectively. The comprehensive analysis of the interaction between 4a to 4f with receptor VEGFR-2 kinase, the result shows compound 4b have higher molecular docking score with receptor. These result well matched with the result of cytotoxicity.
KEYWORDS- 1,4-Benzodiazepine-2,5-diones
- solvent-free synthesis
- cytotoxicity
- molecular simulation