JOURNAL 2609
Organic Communications
Year: 2022 Issue: 4 October-December
p.304 - 323
Viewed 2822 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
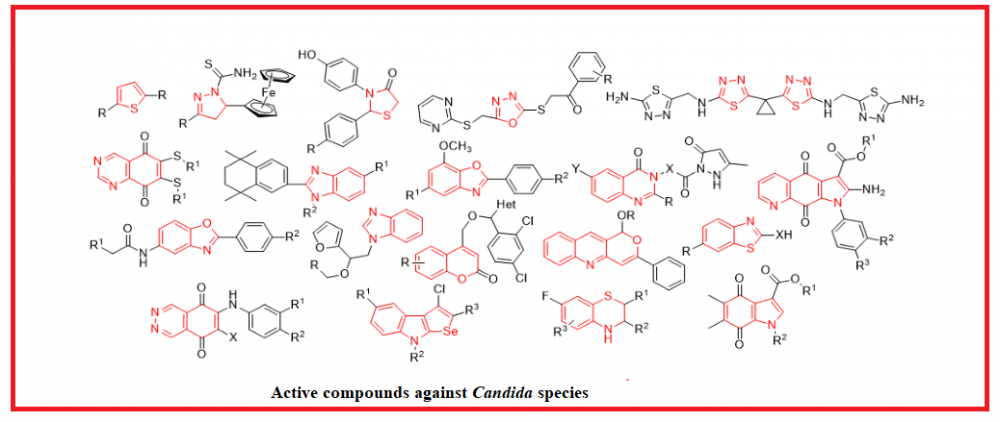
The most common reason for fungal infections is the development of Candida yeasts. Candida naturally is occurs on the skin and on most mucosal surfaces. It is proven that 90% of infections are caused by five Candida species: Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida krusei. Herein we’ve reviewed isolated and fused heterocyclic compounds that exhibit antifungal activity against Candida strains. Over 200 potential fungicidal agents were described, and some of the particularities which affect the action values were determined. Thus, it was noted that the presence of nitro-, methoxy-, trifluoromethyl-, and/or halogeno-containing groups at the specific positions in the benzene ring could significantly increase the inhibition of yeasts growth. That’s why using these patterns together with heterocycles while designing target compounds could speed up the search for new antifungal drugs.
KEYWORDS- Candida sp.
- heterocyclic compounds
- fungicidal drugs
- MIC
- IC50